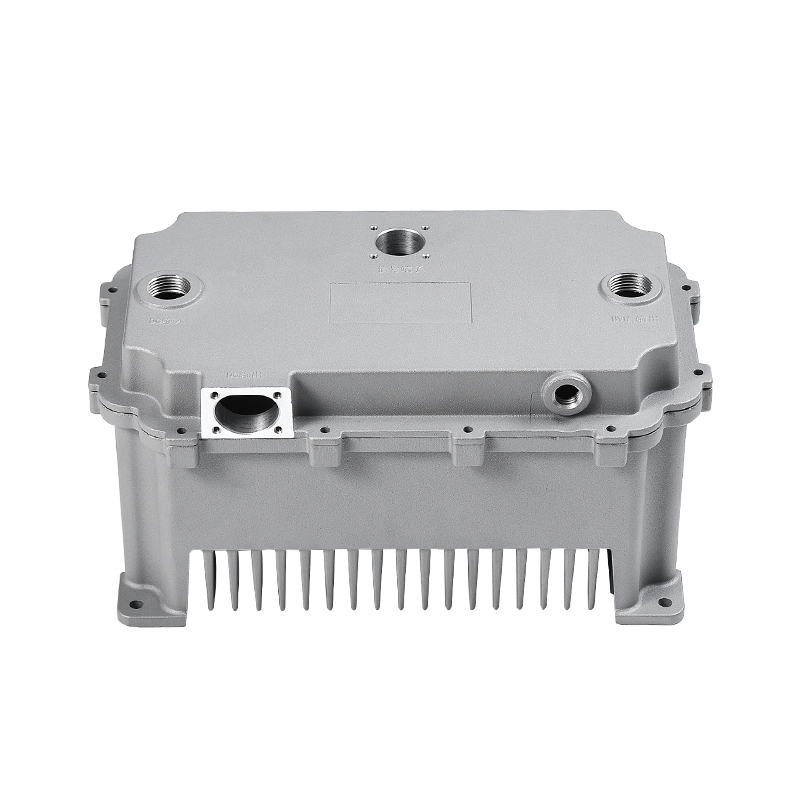
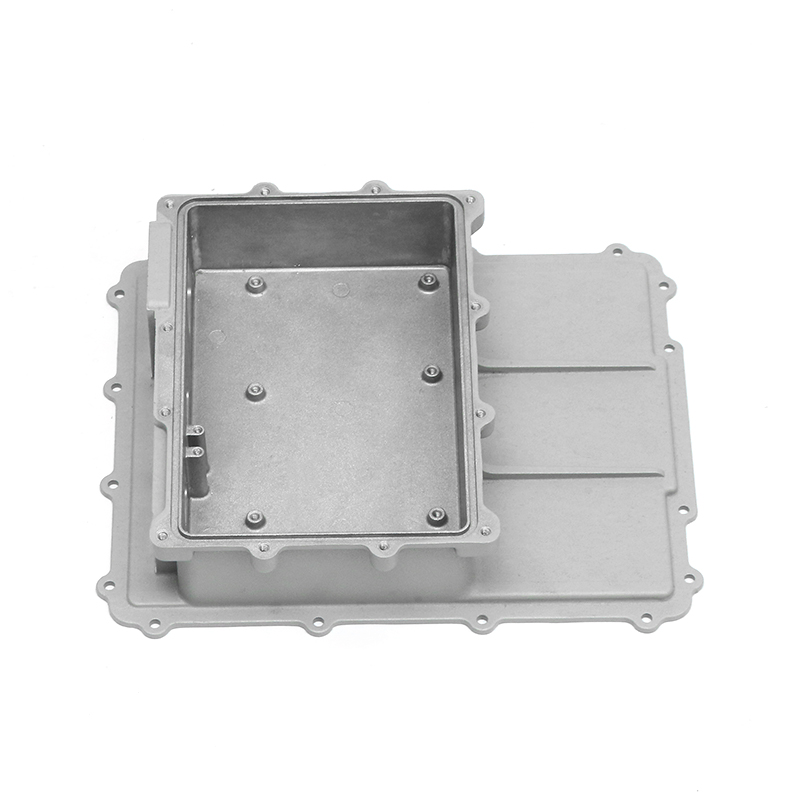
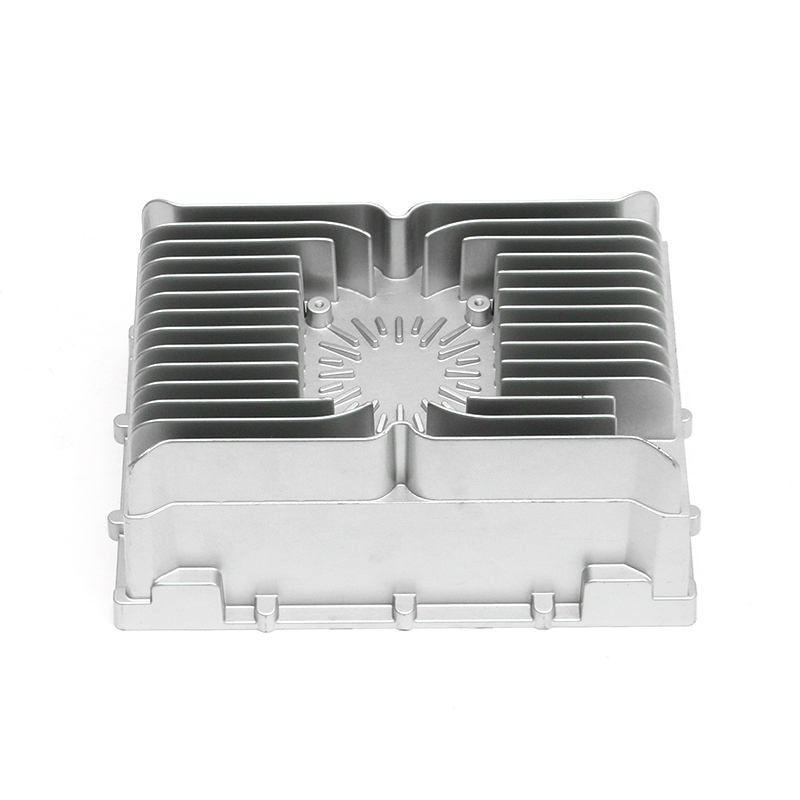
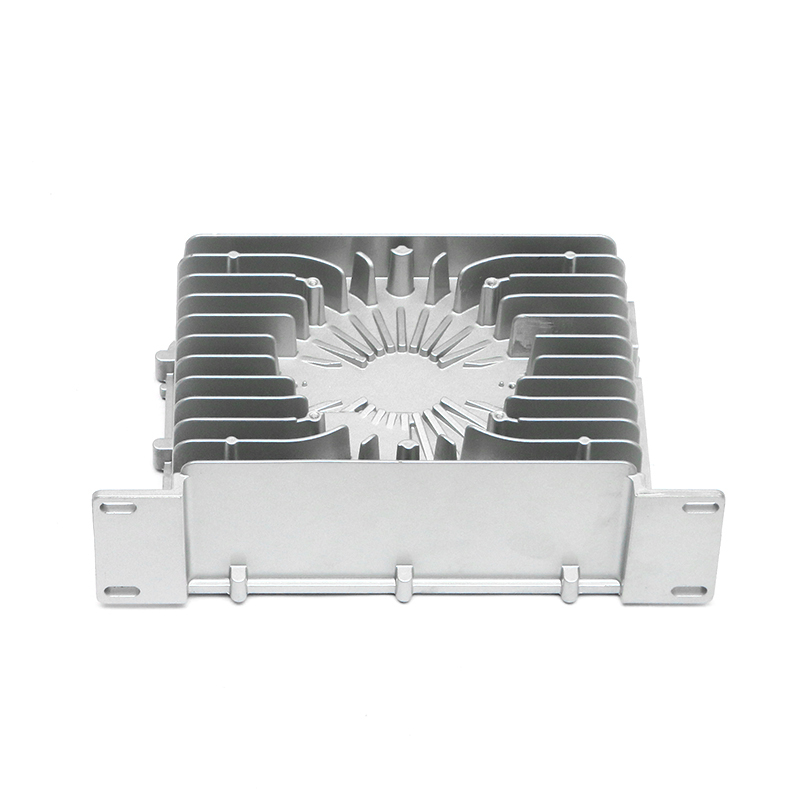
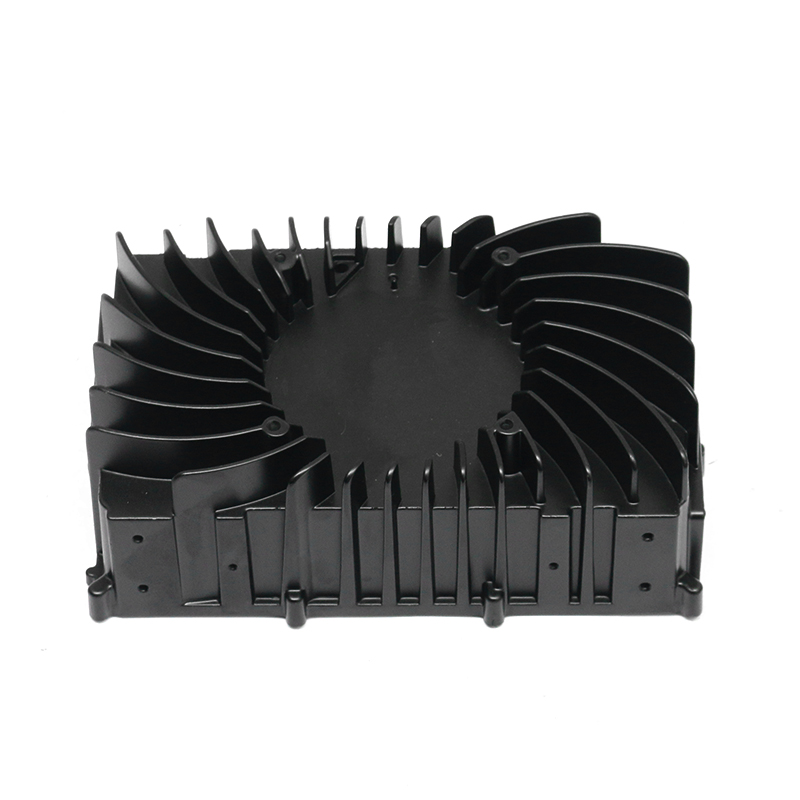
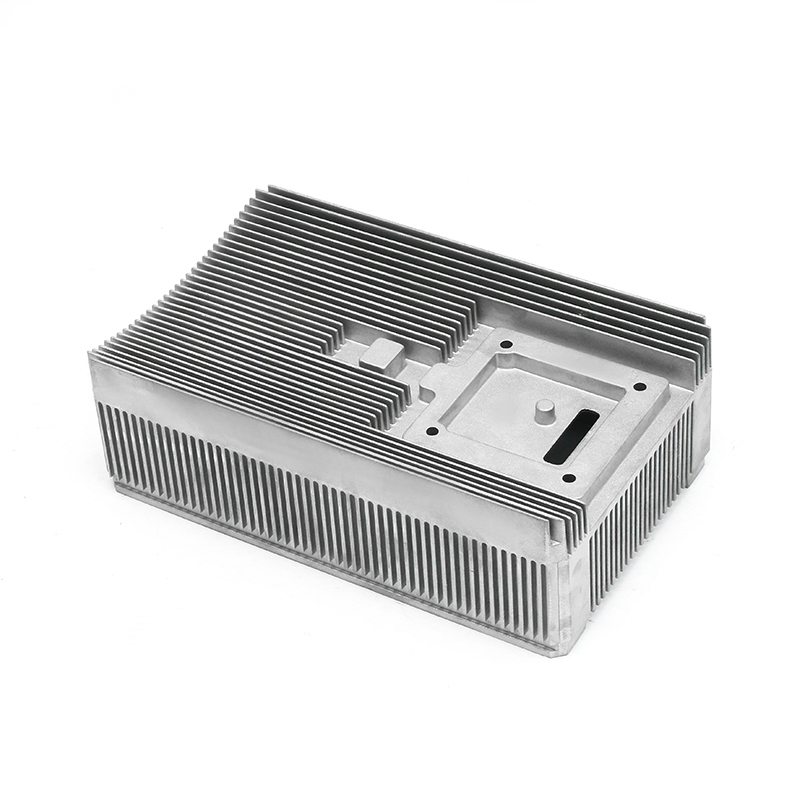
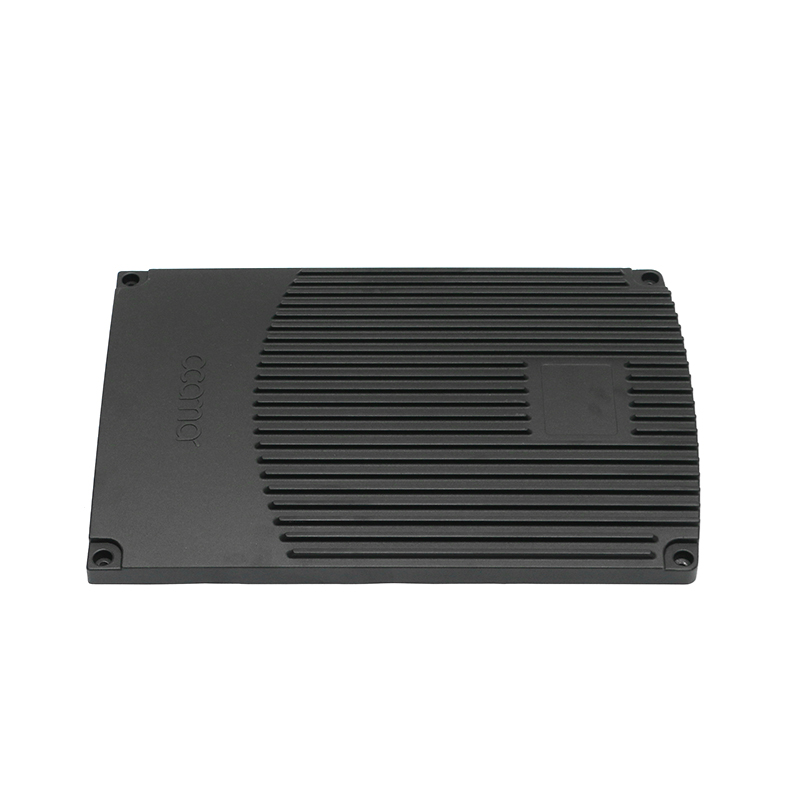
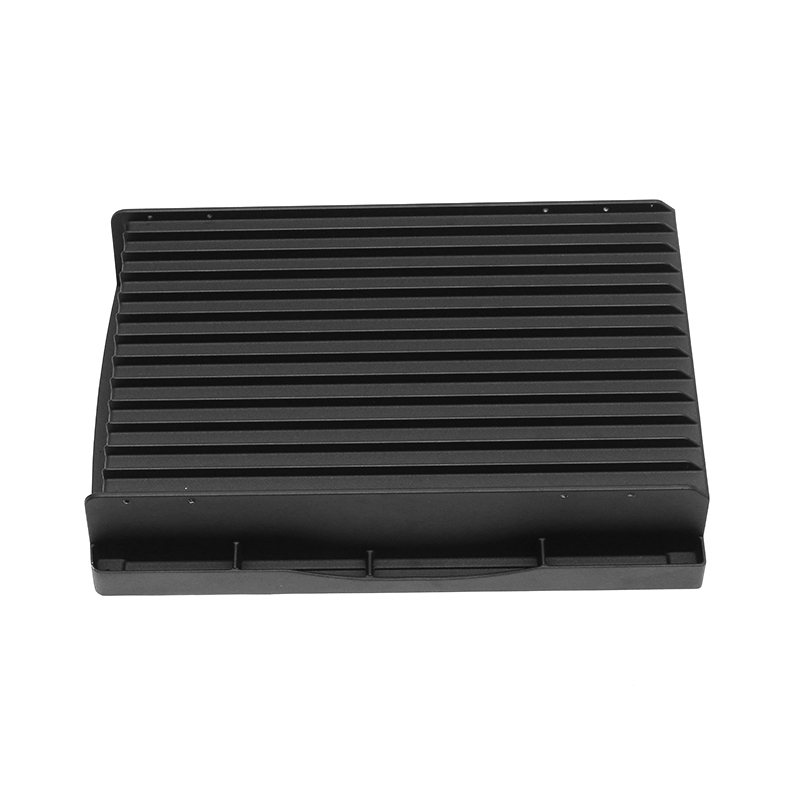
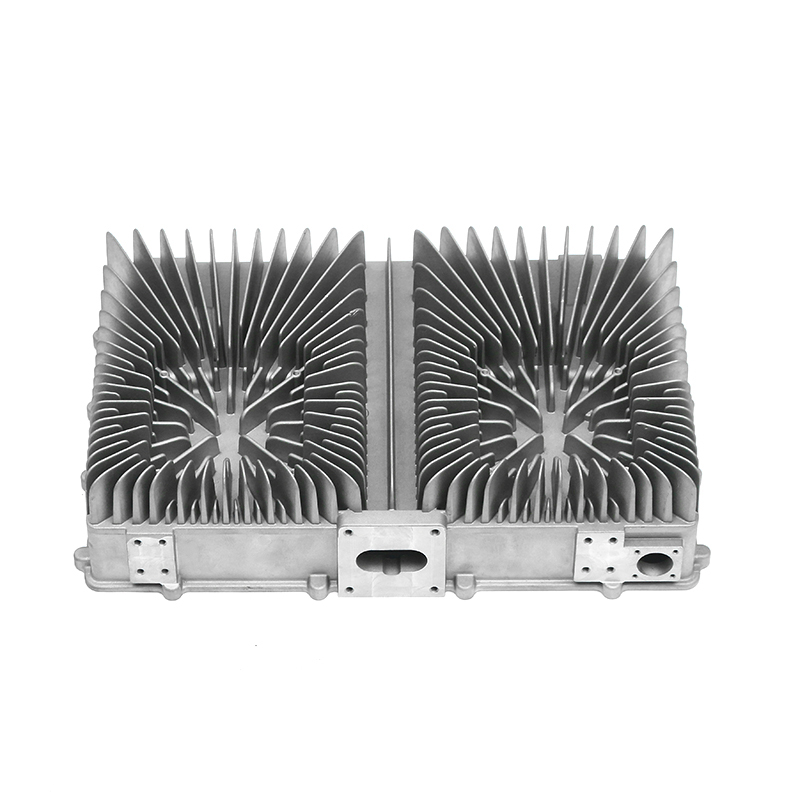
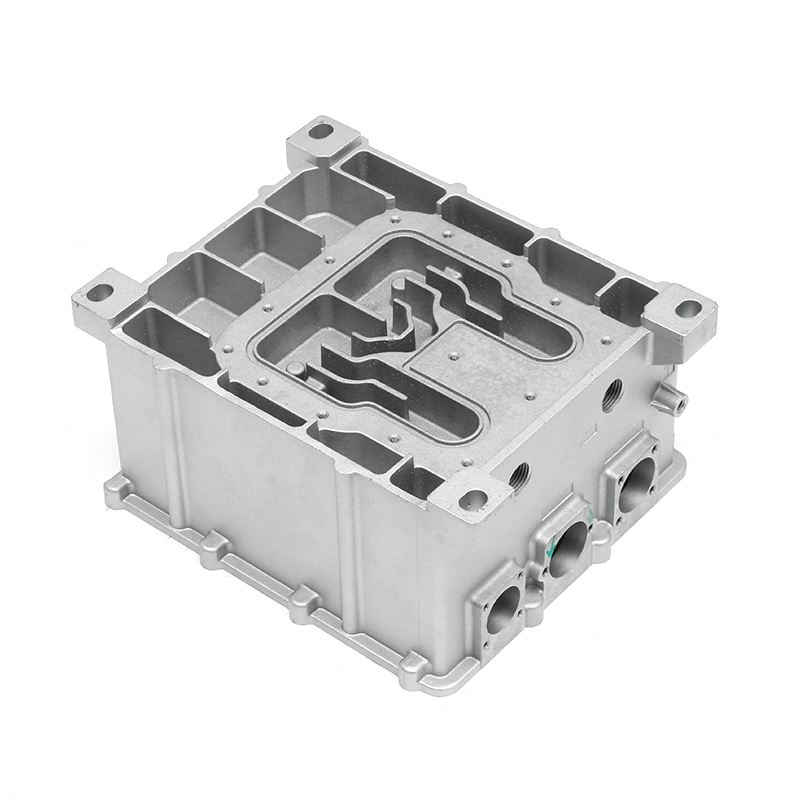
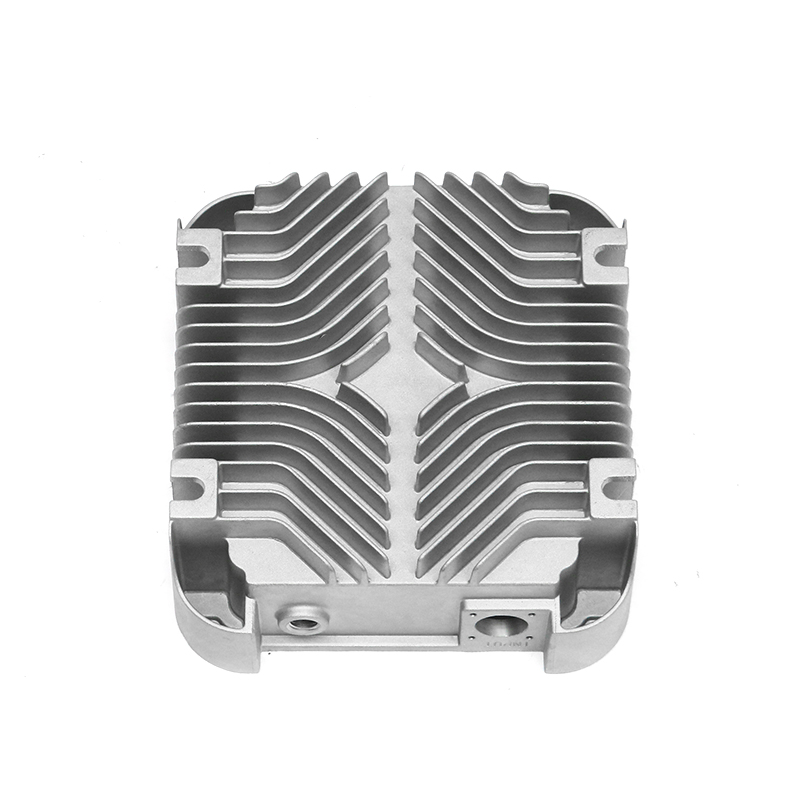
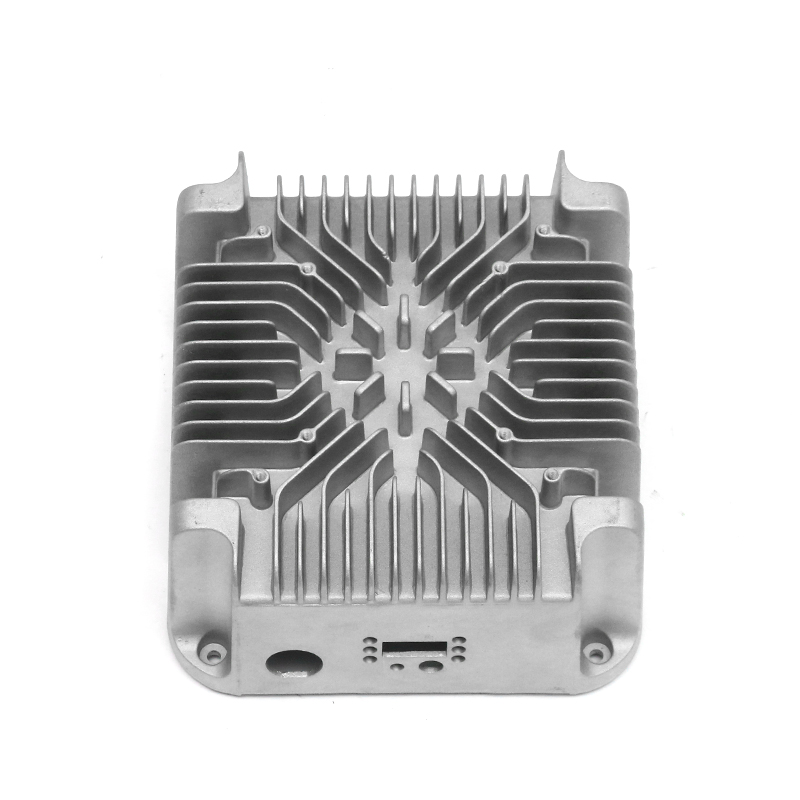
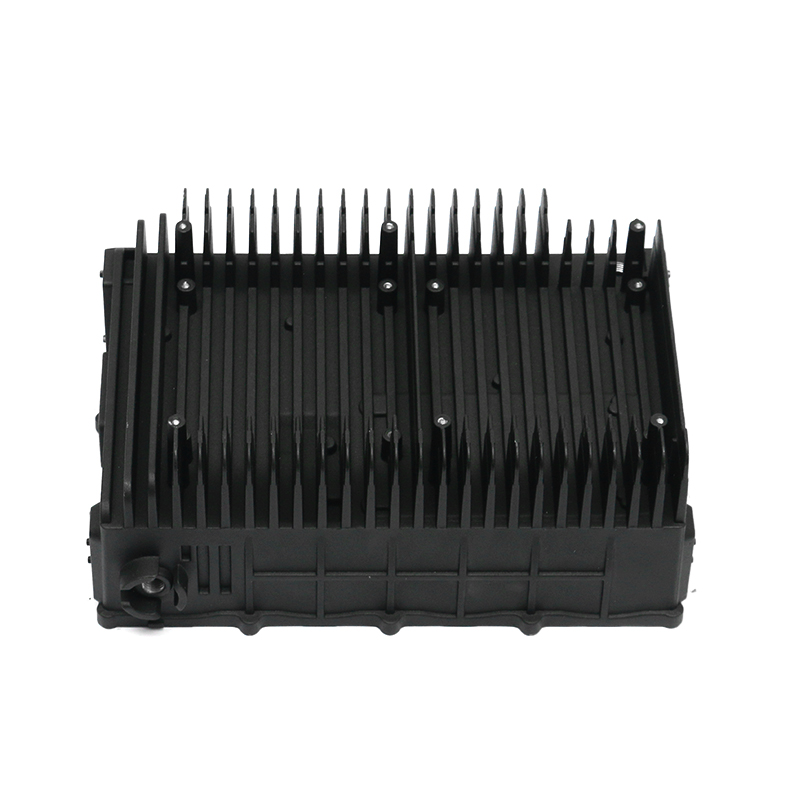
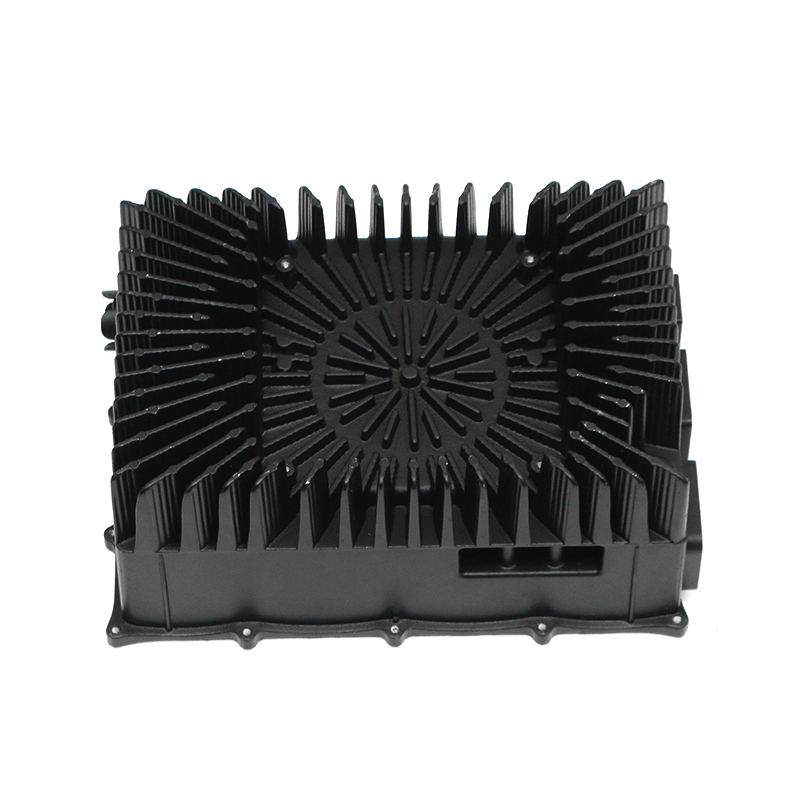
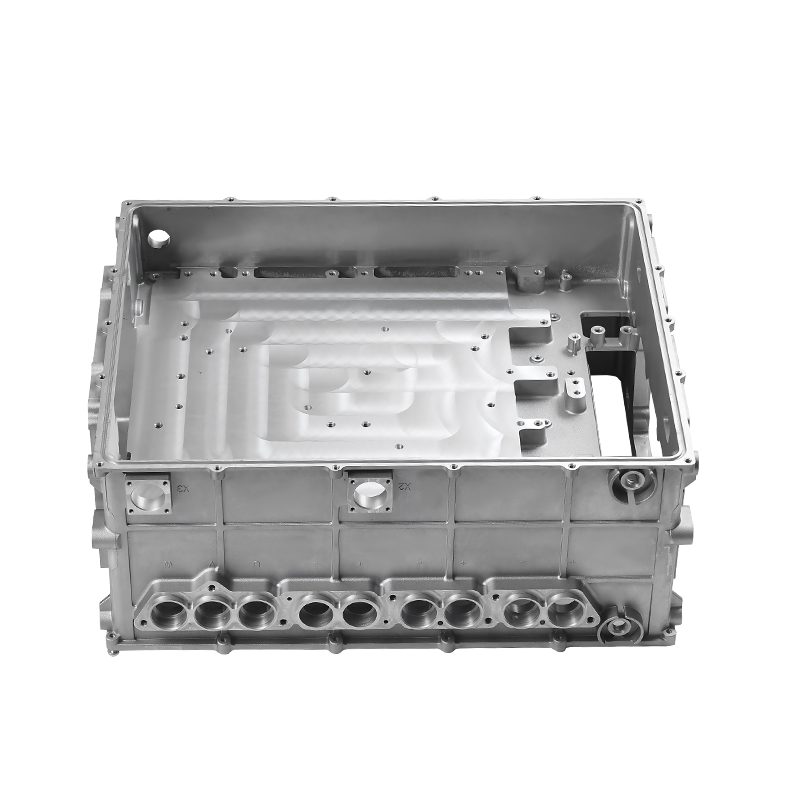
The new energy motor housing die casting plays a significant role in the overall durability and lifespan of the motor by providing structural support, thermal management, and protection against environmental factors. The design, material choice, and manufacturing process of the motor housing directly influence the motor's efficiency, safety, and longevity.
Efficient Heat Transfer: The motor housing often acts as a critical component for managing the motor’s heat. In electric motors, excessive heat can reduce efficiency, accelerate wear and tear, and shorten the motor's lifespan. Die-cast aluminum or magnesium alloys, commonly used in housing, have high thermal conductivity, allowing heat to dissipate quickly from the motor components to the surrounding environment.
Heat Sink Features: Motor housings designed with integrated fins or channels improve heat dissipation. These features increase the surface area of the housing, allowing for more efficient heat release, which helps prevent overheating of the motor during prolonged use, contributing to a longer service life.
Prevention of Thermal Expansion: High-quality die-casting ensures that the housing can withstand the thermal expansion and contraction that occurs as the motor heats up and cools down. This resilience prevents deformation or cracking over time, which could otherwise lead to motor damage or failure.
Resistance to Moisture, Dust, and Chemicals: Die-cast motor housings are often designed with sealed and robust structures that provide protection against environmental contaminants. The sealed nature of the die-cast housing prevents the ingress of dust, dirt, and moisture, which could otherwise damage internal components, corrode the motor, or lead to electrical shorts.
Corrosion Resistance: Materials such as aluminum alloys or magnesium alloys are commonly used in die-casting because of their natural corrosion resistance. These materials resist the effects of rust and corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, salt, and other corrosive elements, which helps extend the motor's lifespan.
Impact Resistance: The die-casting process produces a motor housing that is not only lightweight but also strong and durable. This structural integrity is essential to protect sensitive motor components from impacts, vibrations, and external forces. The housing ensures that the motor is shielded from damage caused by physical shocks or vibrations, which could otherwise compromise the motor’s internal structure.
Maintaining Alignment: The die-cast housing helps maintain the precise alignment of the motor's internal components, such as the rotor and stator. Proper alignment ensures that the motor operates efficiently, reducing unnecessary wear, friction, and vibration that can shorten the motor’s lifespan.
High-Quality Alloys: The materials commonly used in new energy motor housing die casting, such as aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys, are chosen for their strength-to-weight ratio and their ability to withstand the stresses that come with long-term use. These materials are also resistant to thermal fatigue, which helps maintain the integrity of the motor housing over time.
Uniformity in Material Properties: The die-casting process allows for the creation of motor housings with uniform material properties, which ensures consistency in performance and longevity. The casting process ensures that the material density and quality are optimized, preventing weaknesses like air pockets or voids, which could compromise the durability of the housing.
Recommended Products
Products provided by famous enterprises are deeply trusted by users.