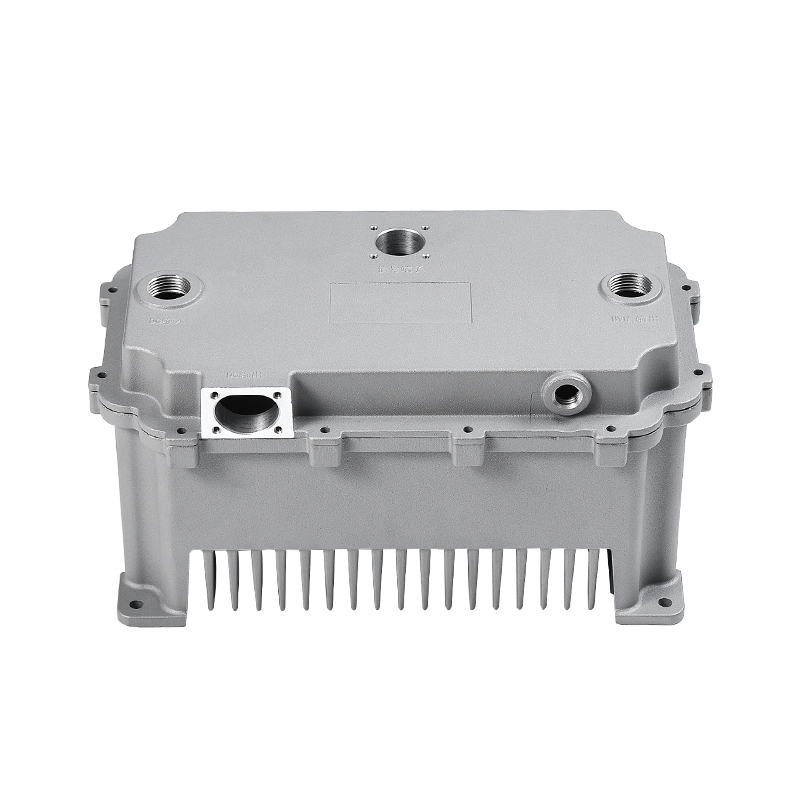
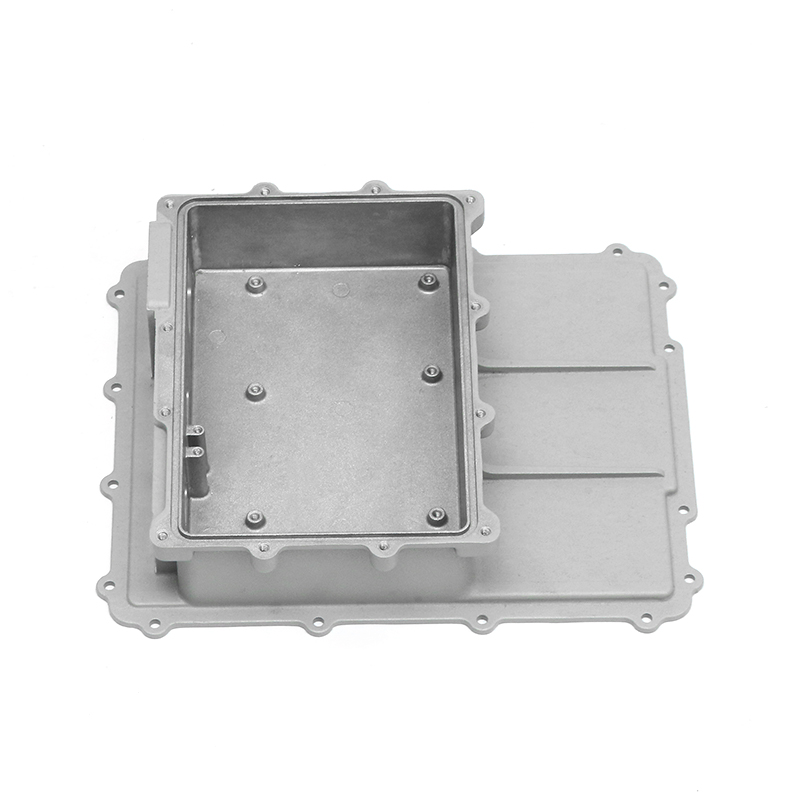
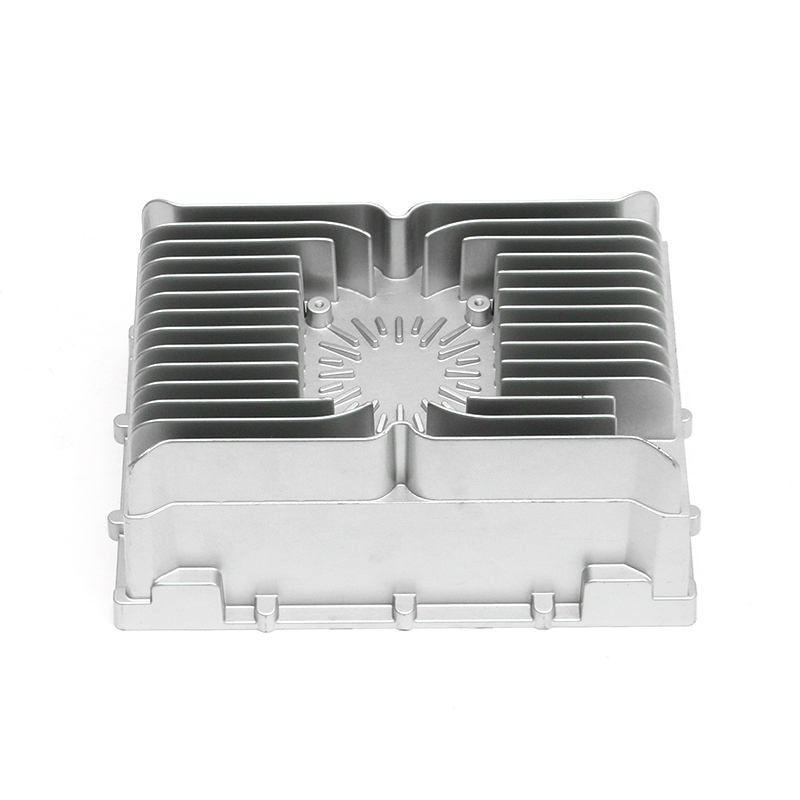
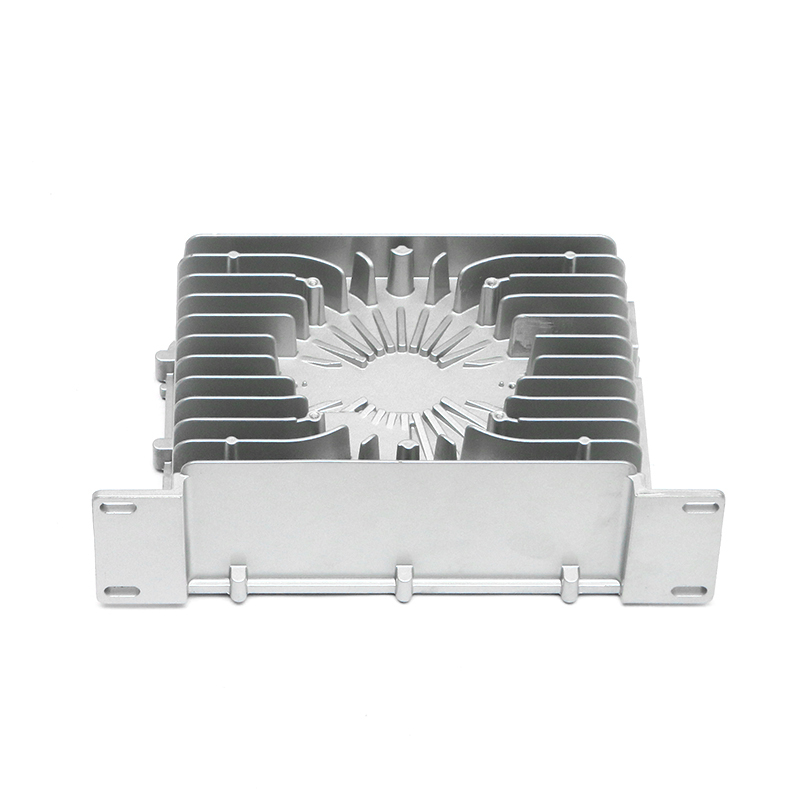
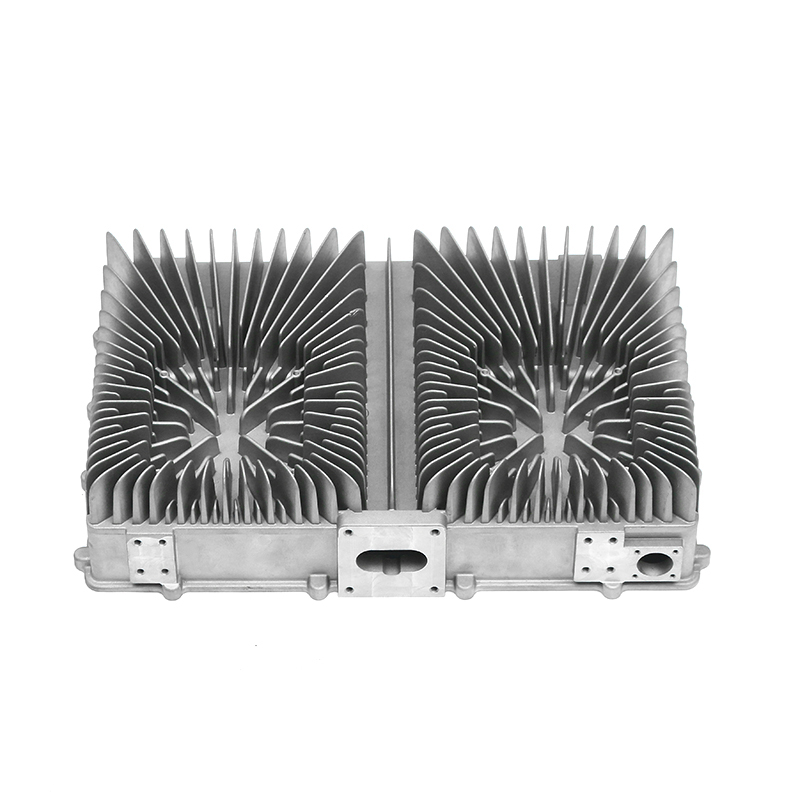
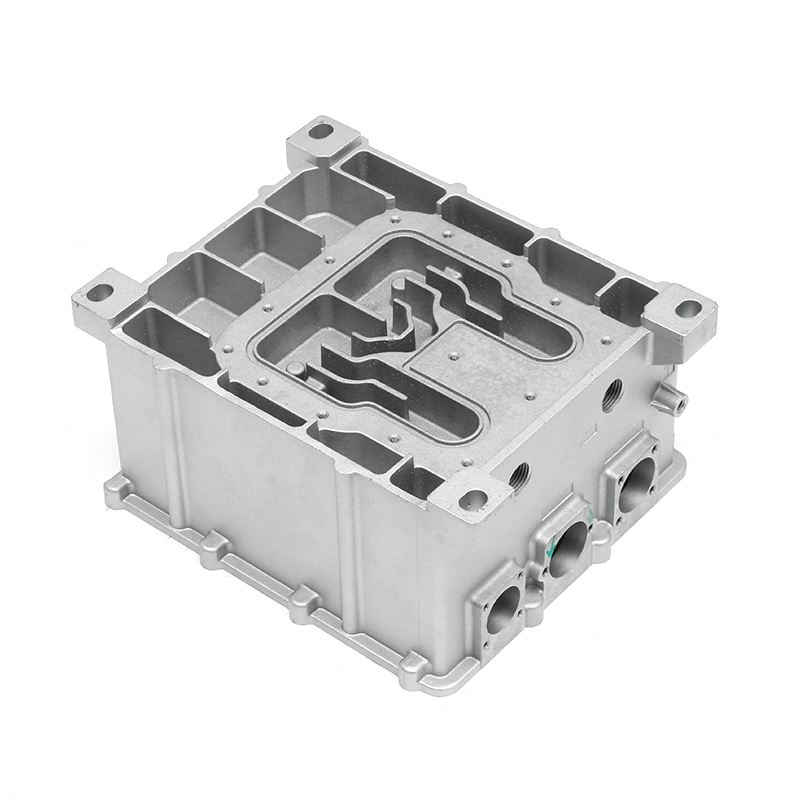
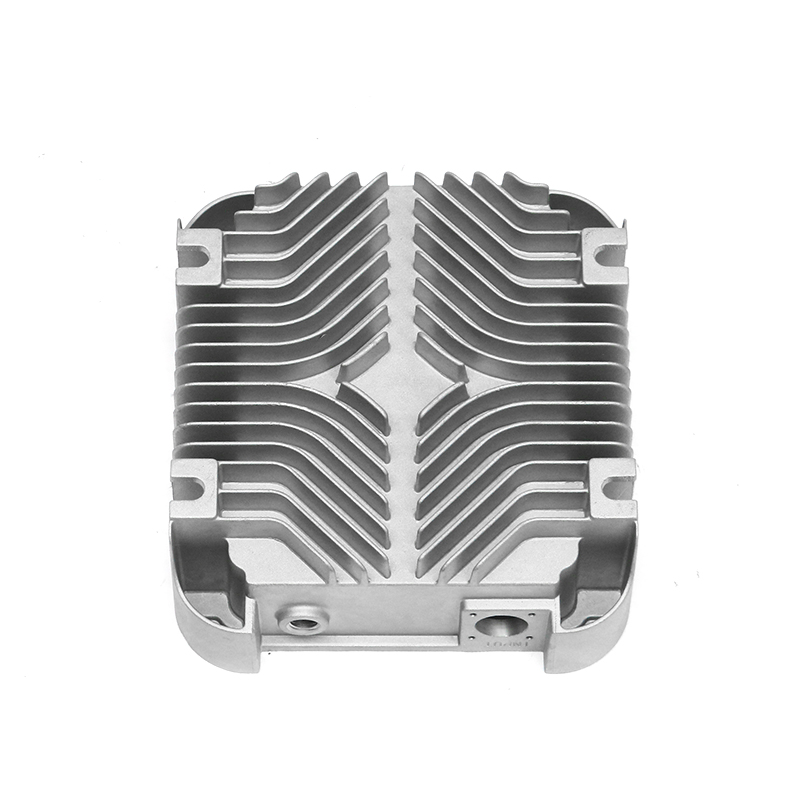
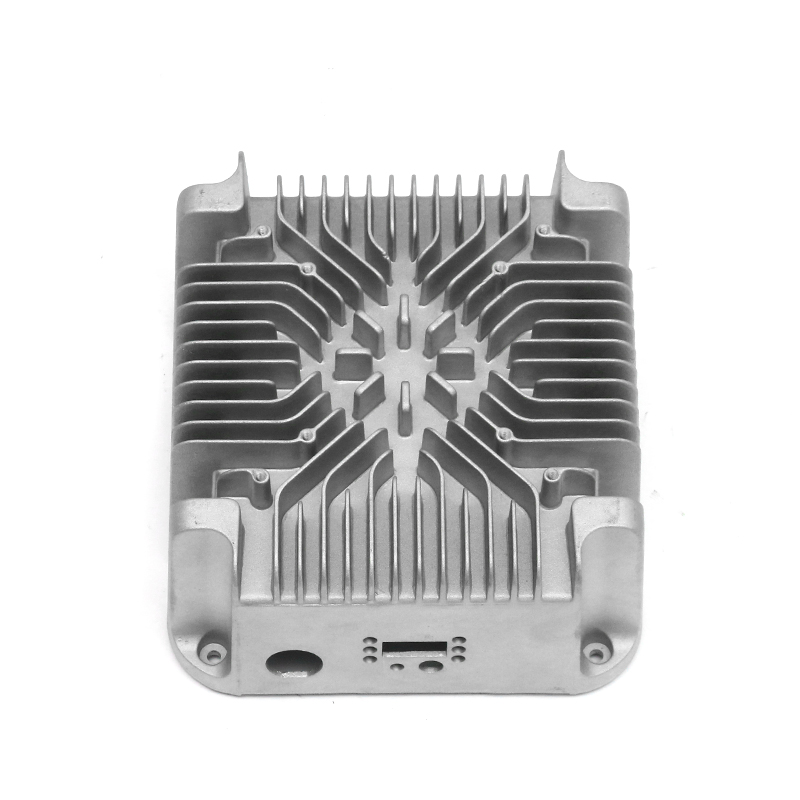
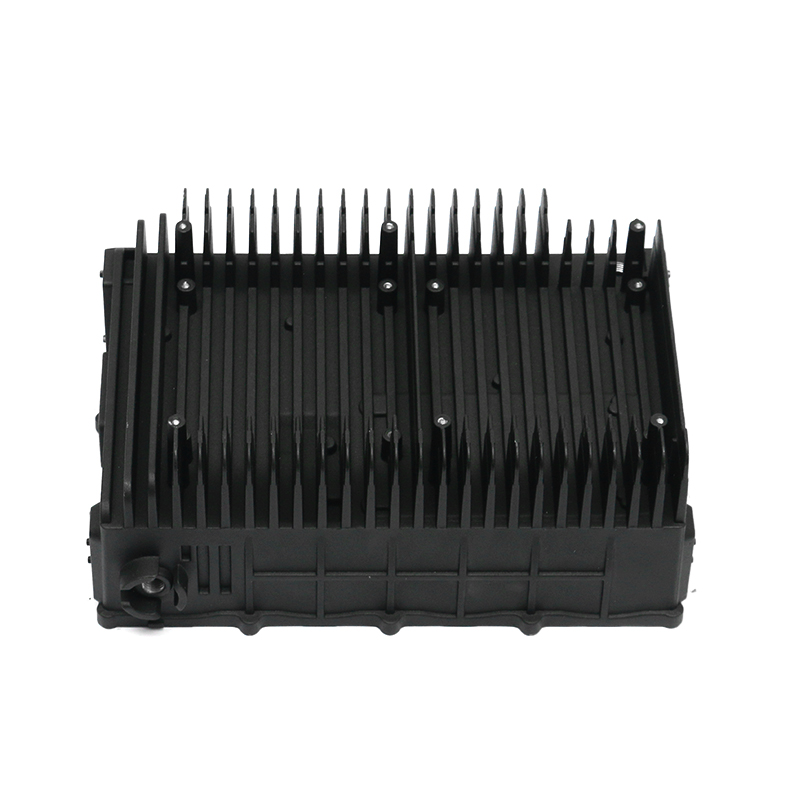
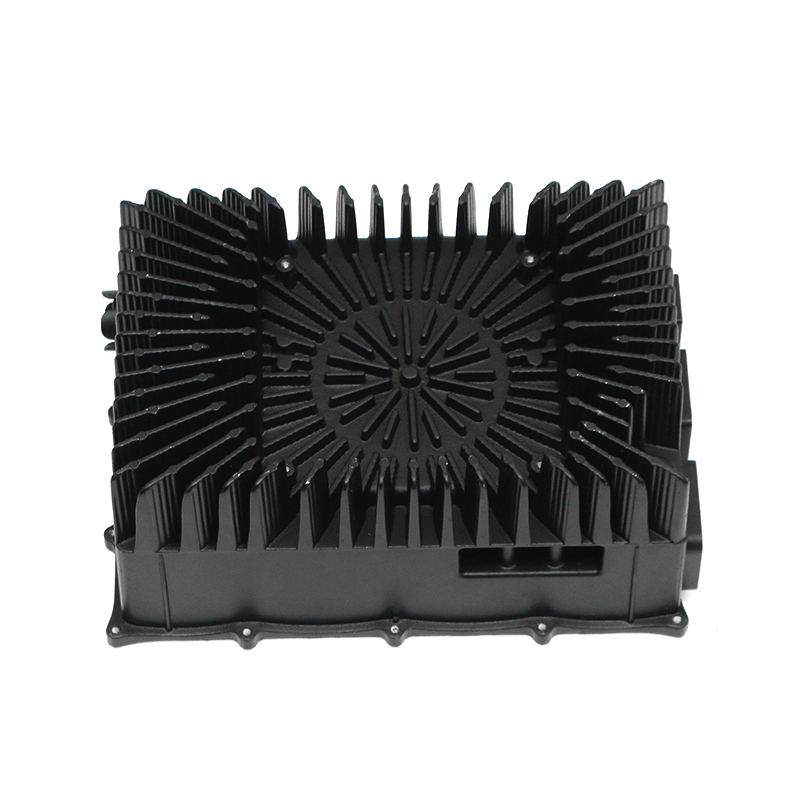
When selecting materials for electronically controlled air-cooling molds for new energy vehicles, you need to consider the following key factors:
Wear resistance: The mold may come into contact with hard materials during the production process, so materials with good wear resistance need to be selected to ensure the life and stability of the mold. Common wear-resistant materials include tool steel, carbide, etc.
High-temperature oxidation resistance: Electronically controlled air-cooled molds may be affected by high-temperature environments during work. Therefore, materials with good high-temperature oxidation resistance need to be selected to ensure the stability and life of the mold at high temperatures. Some high-temperature alloys such as hot tool steel, high-speed steel, etc. have better high-temperature properties.
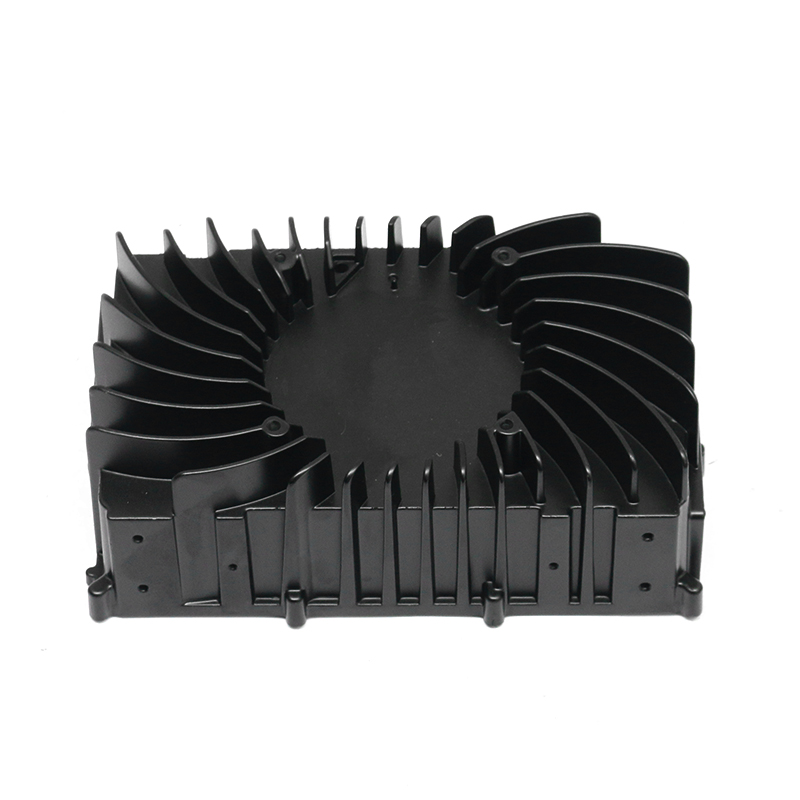
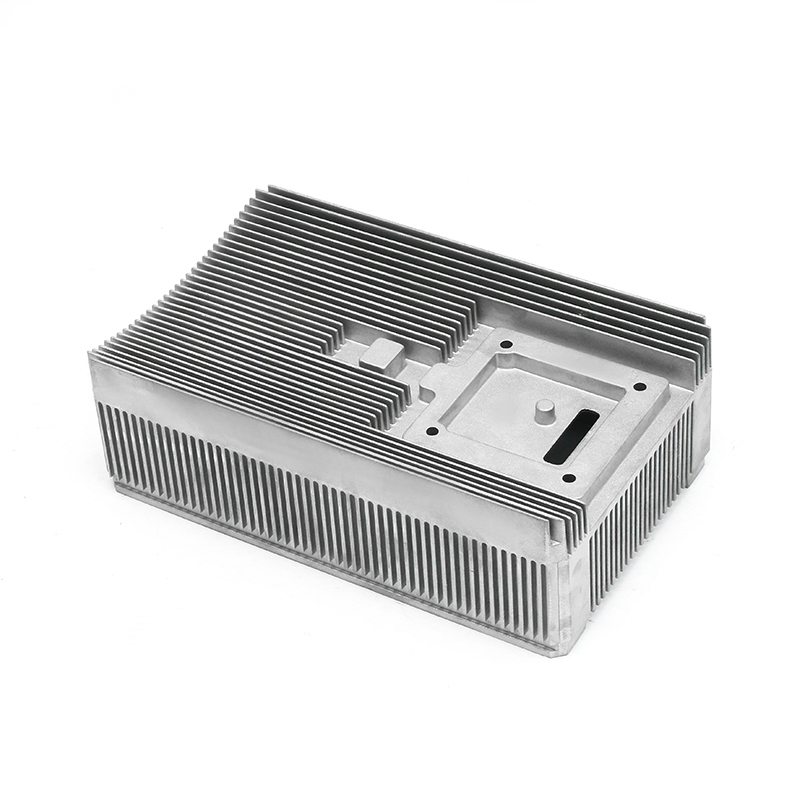
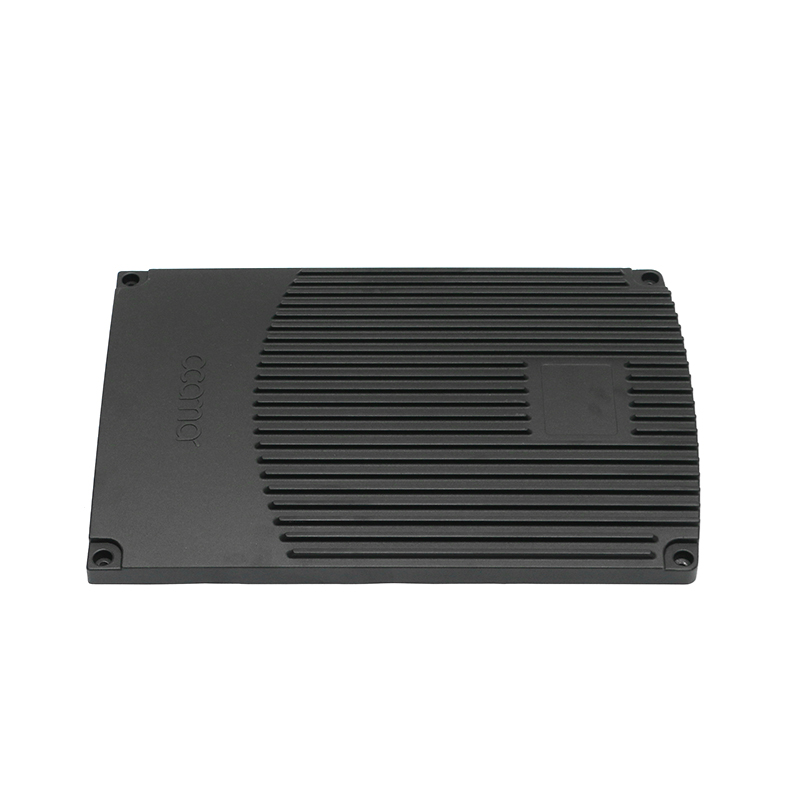
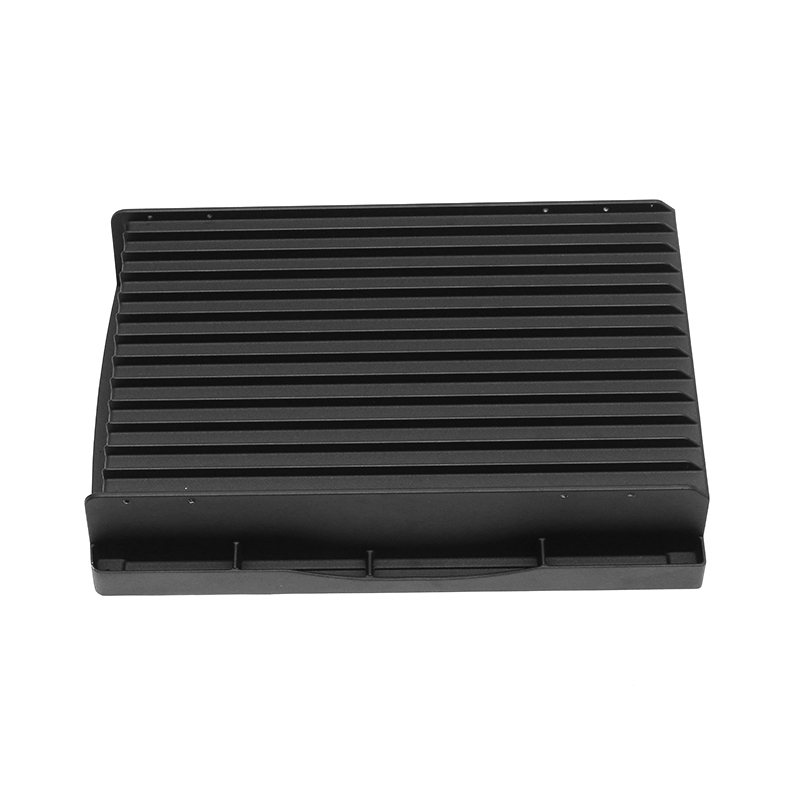
Thermal conductivity: Electronically controlled air-cooled molds need to have good thermal conductivity to quickly dissipate heat and ensure temperature control of electronic components. Materials with good thermal conductivity such as aluminum alloys are often used to manufacture heat dissipation structural components.
High strength: Molds need to be strong enough to withstand the forces and pressures during processing, as well as the loads during long-term use. Materials with high strength and toughness such as tool steel and alloy steel are often chosen.
Corrosion resistance: Electronically controlled air-cooled molds may be exposed to corrosive media or affected by environmental factors such as humidity, so materials with good corrosion resistance need to be selected to avoid corrosion and damage to the mold. Materials with good corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel, are often chosen.
Processing performance: The processing performance of the material is also one of the factors considered. The mold manufacturing process may require cutting, milling, drilling and other processing operations, so it is necessary to choose materials that are easy to process to improve manufacturing efficiency.
Taking the above factors into consideration, common material choices include tool steel (such as D2, H13), carbide, high-speed steel, aluminum alloy and stainless steel. Specific selections should be evaluated based on the mold's design requirements, operating environment, and expected performance. For electronically controlled air-cooled molds with special requirements, composite materials or special alloys may also be needed to meet specific process and performance requirements.
Recommended Products
Products provided by famous enterprises are deeply trusted by users.