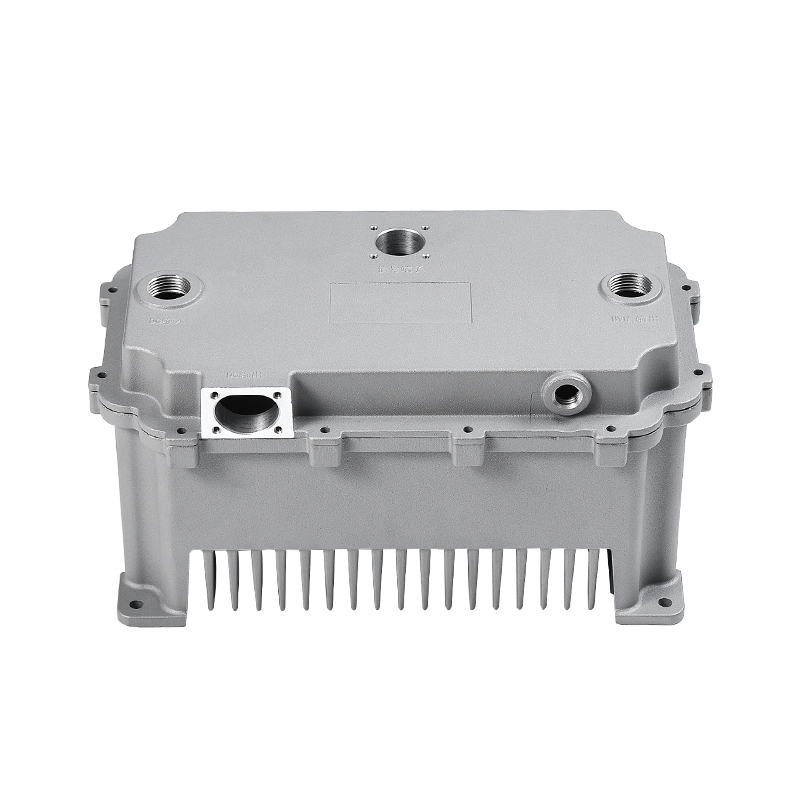
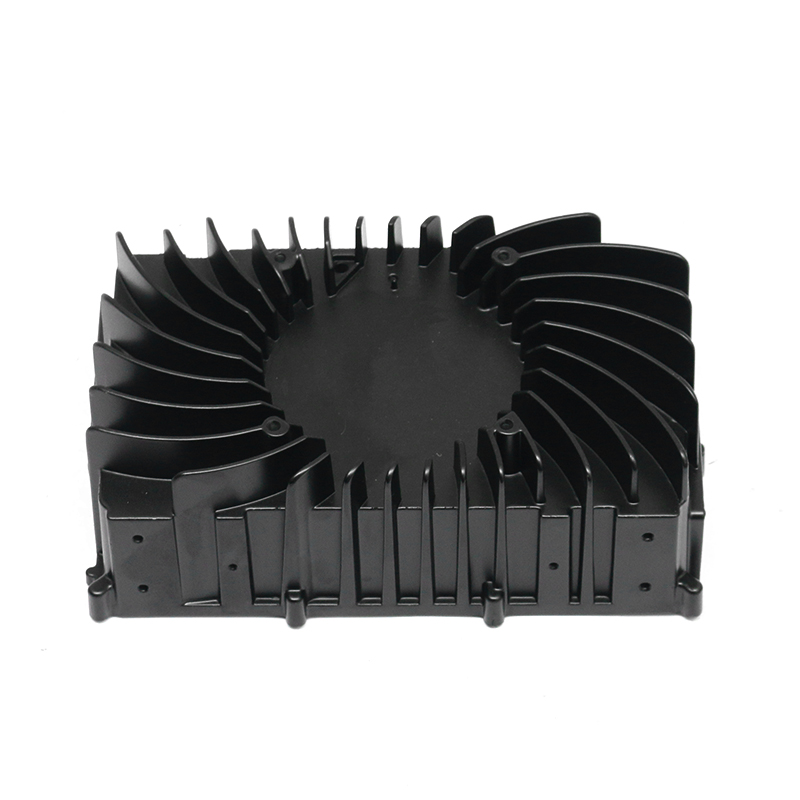
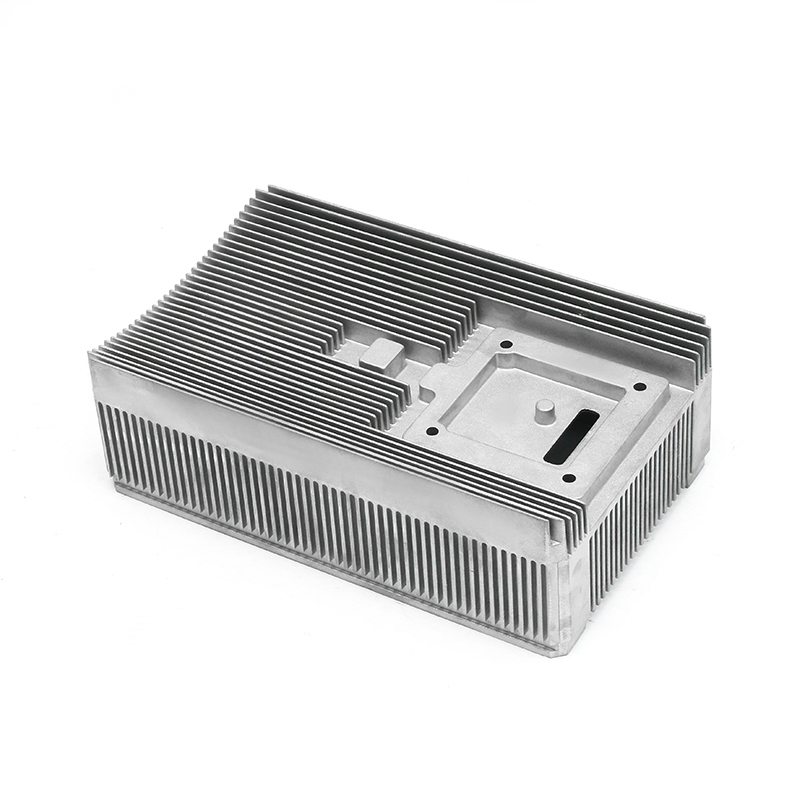
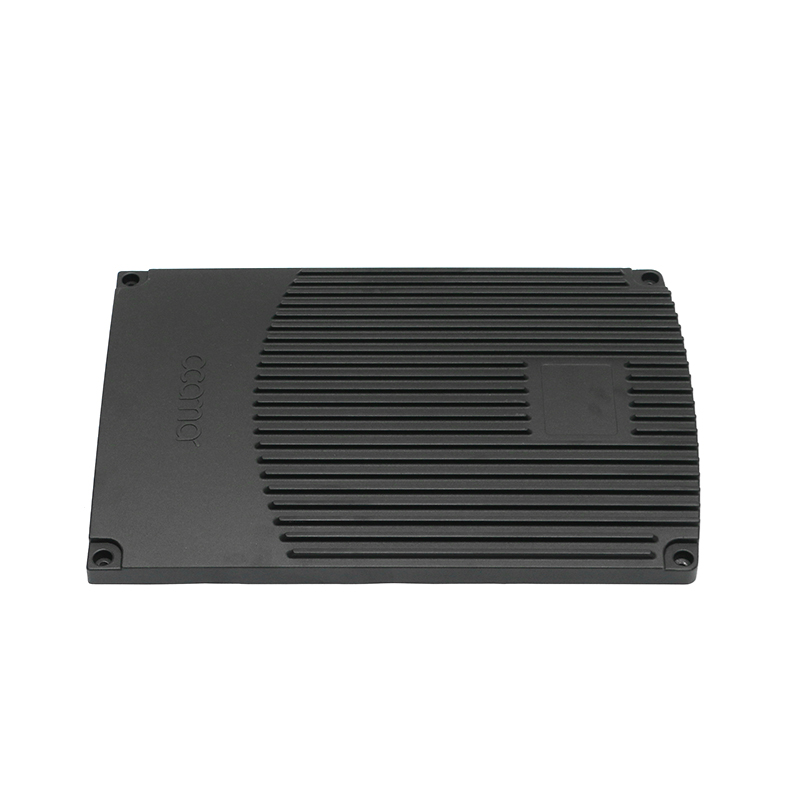
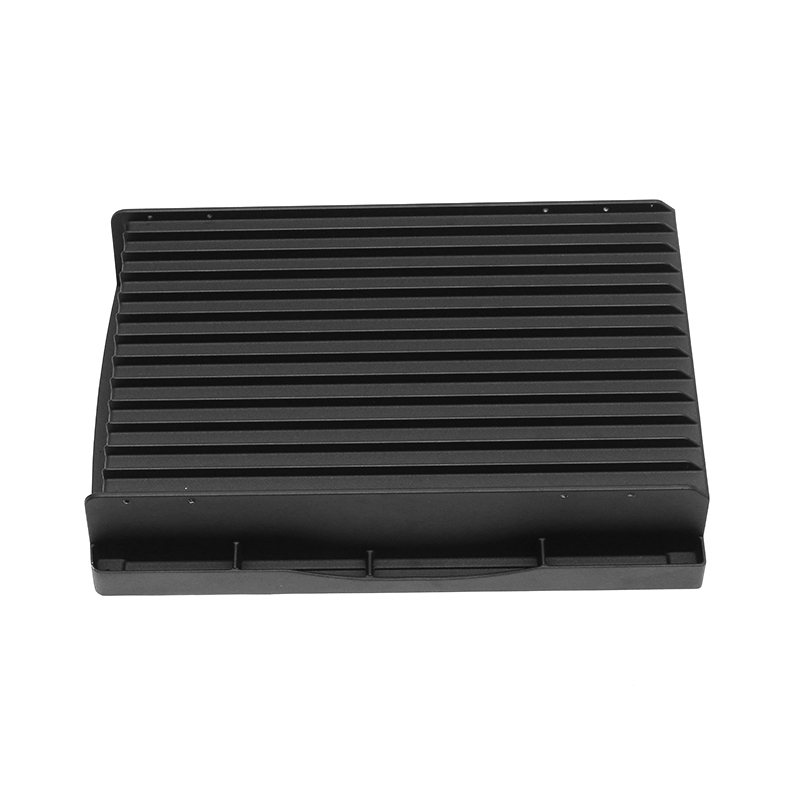
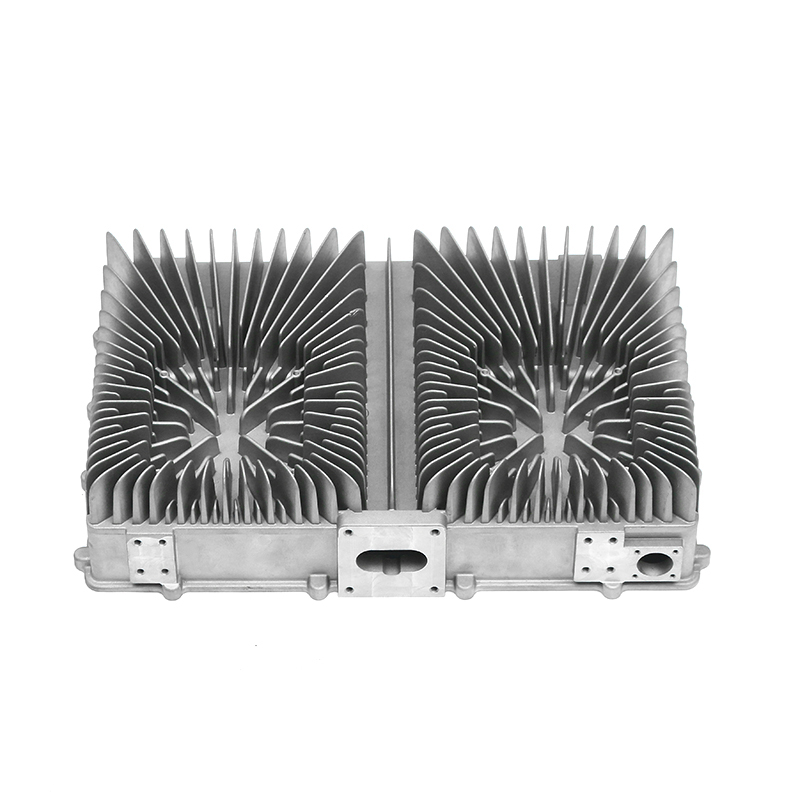
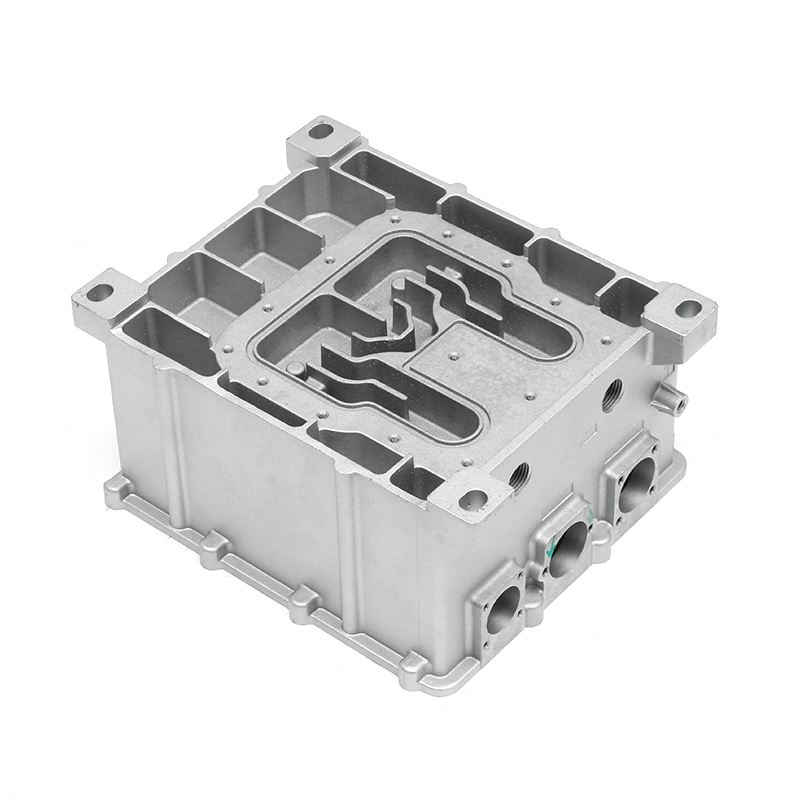
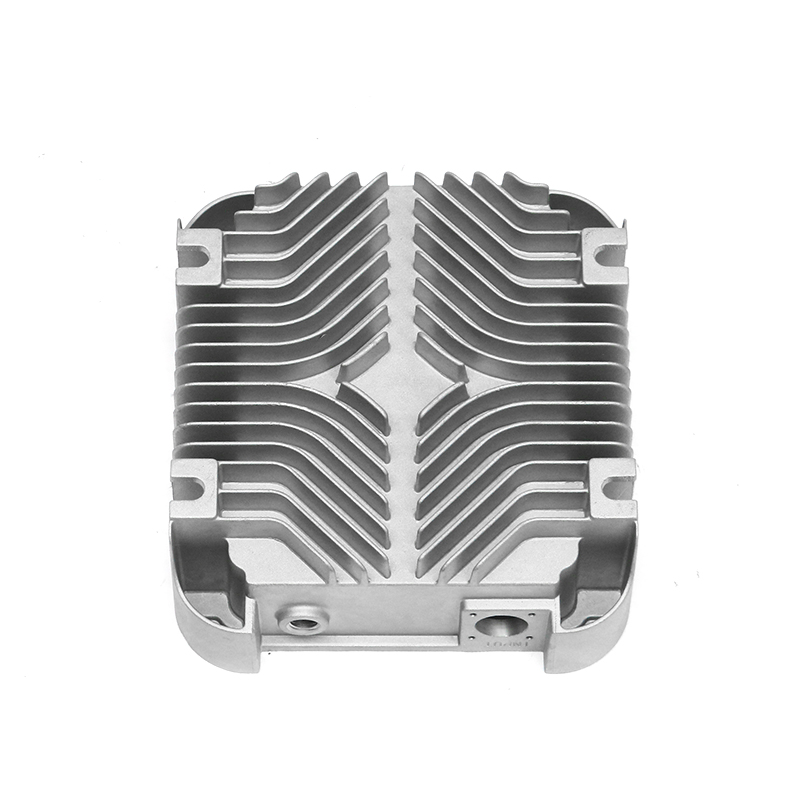
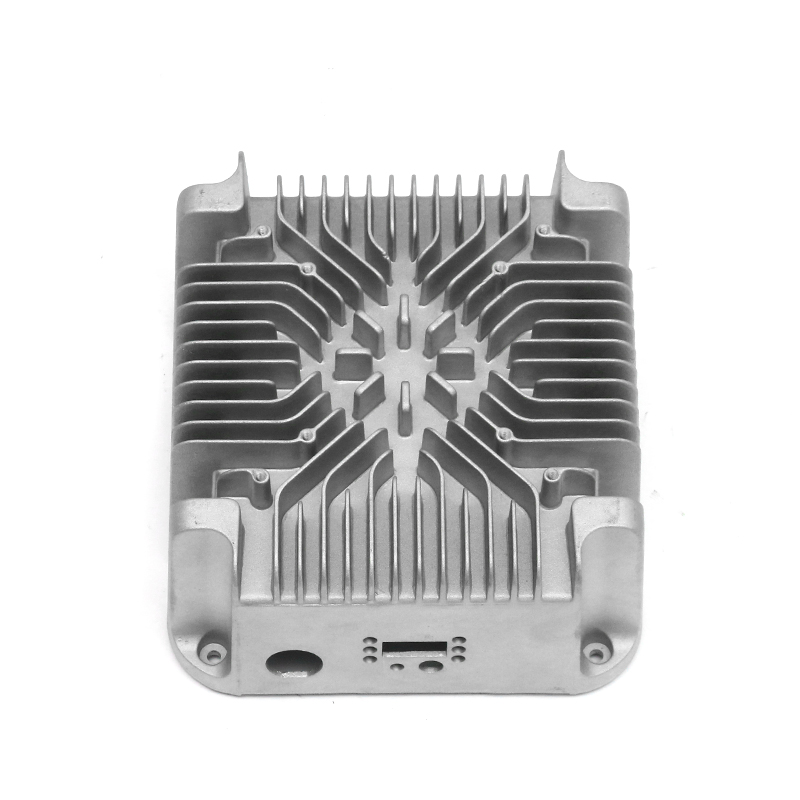
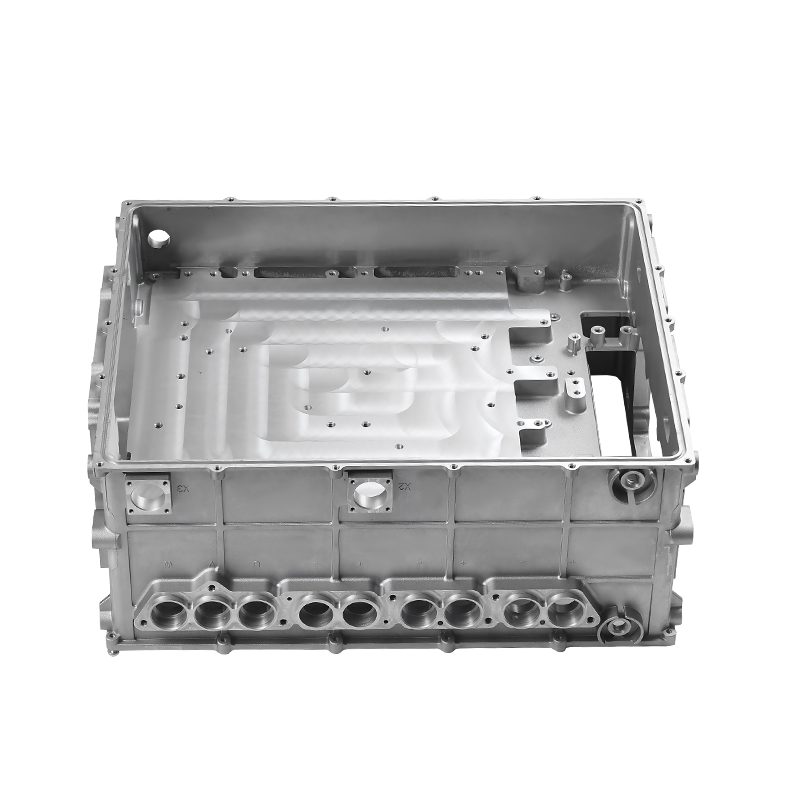
Containment of Lubricant: Gearbox housings are meticulously designed to provide a secure enclosure for the lubricant used within the gearbox assembly. This containment is paramount as it prevents any leakage of lubricant, which could otherwise lead to operational inefficiencies, increased friction, and potential damage to internal components. The housing is engineered with tight tolerances and robust sealing mechanisms to maintain an airtight environment, ensuring that the lubricant remains within the gearbox and is continuously available to lubricate moving parts.
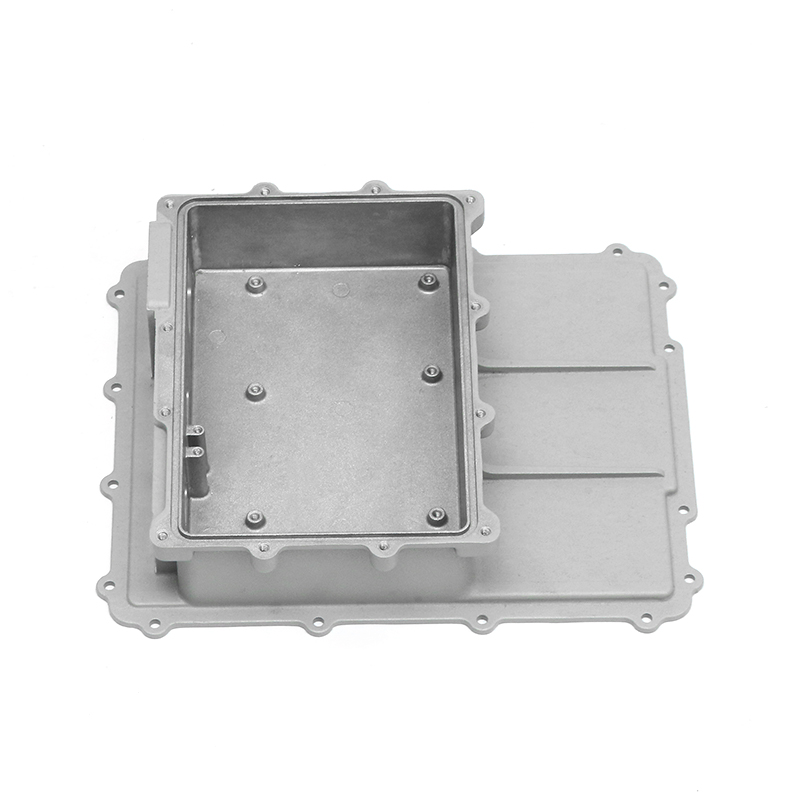
Distribution of Lubricant: Inside the gearbox housing, a sophisticated network of channels, galleries, and reservoirs is strategically integrated to facilitate the efficient distribution of lubricant throughout the gearbox assembly. This distribution system is meticulously designed to ensure that lubricant reaches every critical component, including gears, bearings, shafts, and other moving parts. By evenly distributing the lubricant, the gearbox housing minimizes frictional losses, reduces wear on components, and optimizes the overall efficiency and performance of the gearbox. This ensures smoother operation, quieter running, and longer service life for the gearbox assembly.
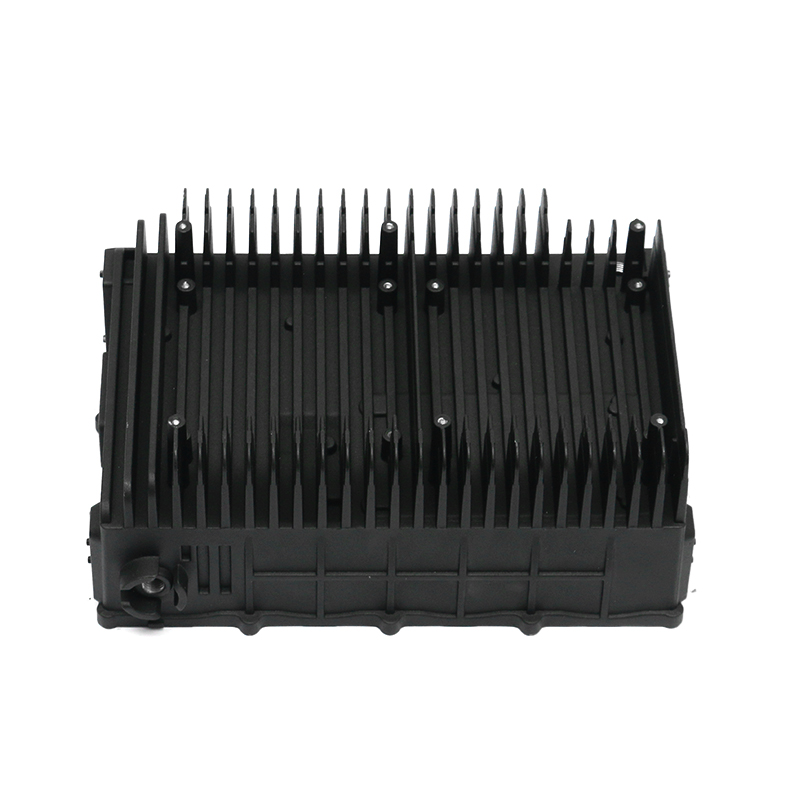
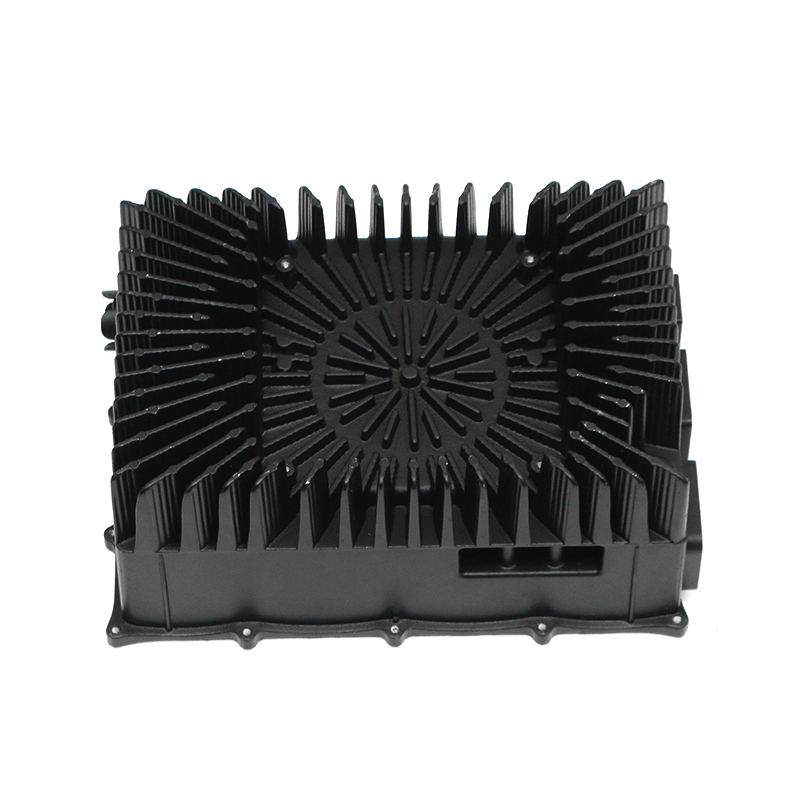
Sealing Mechanism: The crucial aspect of gearbox housing design is its sealing mechanism, which plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of the lubrication system. High-quality seals and gaskets are strategically placed at key interfaces within the housing to prevent the ingress of contaminants such as dust, dirt, water, and debris. These seals create a robust barrier that effectively seals off the gearbox internals from external elements, ensuring that the lubricant remains clean and uncontaminated. By safeguarding the lubrication system, the housing prolongs the life of internal components, enhances operational reliability, and reduces the need for frequent maintenance interventions.
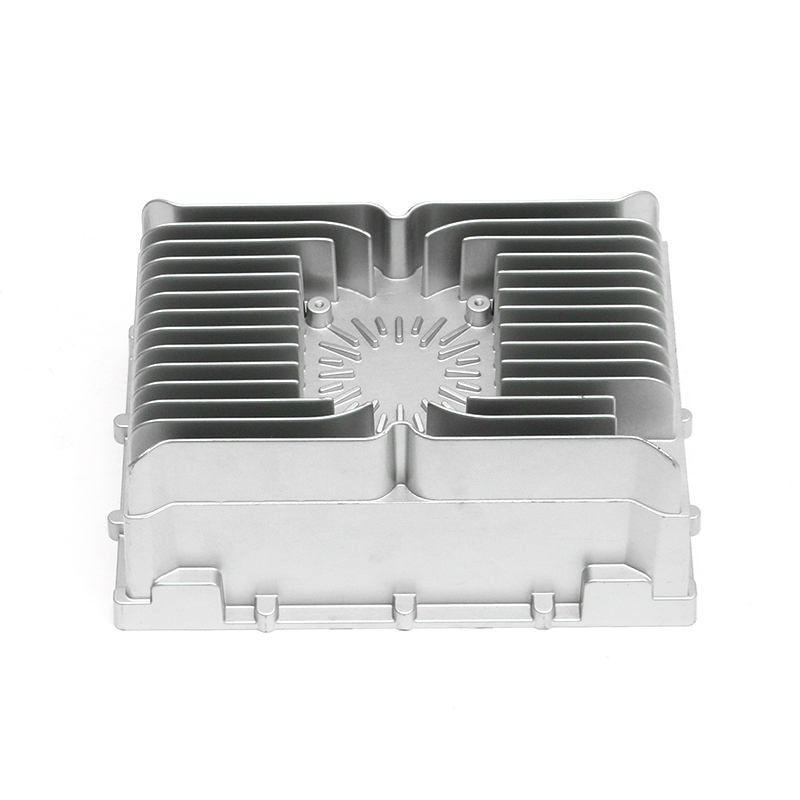
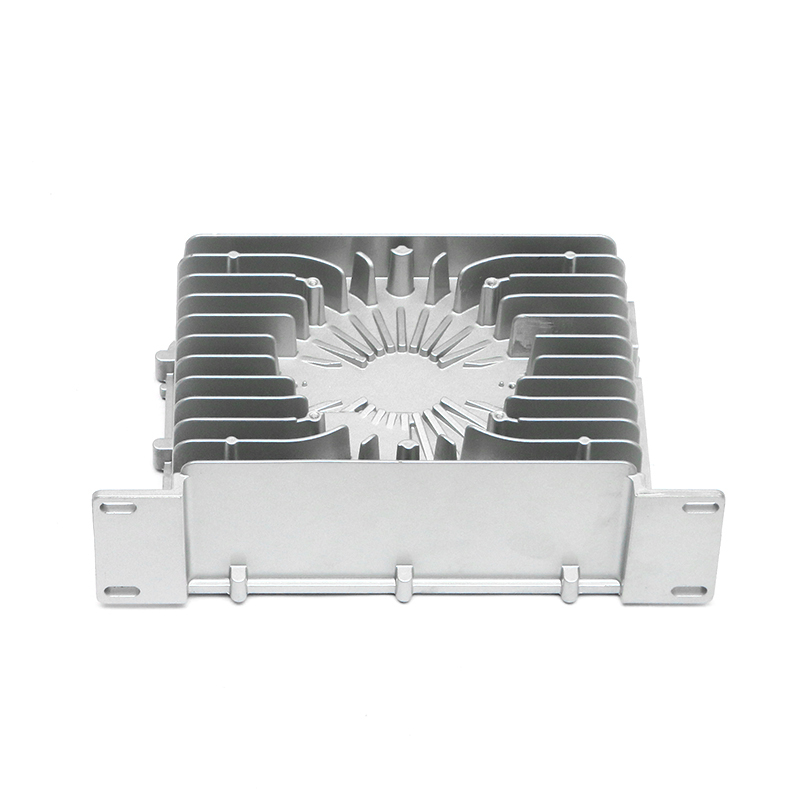
Heat Dissipation: During operation, gearboxes generate significant heat due to the mechanical friction and movement of components. The gearbox housing is ingeniously designed to facilitate effective heat dissipation from the internal components. This is achieved through several mechanisms, including the use of heat sinks, cooling fins, integrated cooling channels, or contact with external cooling systems. By efficiently dissipating heat away from critical components, the housing helps maintain the optimal operating temperature of the lubricant. This thermal management not only preserves the viscosity and lubricating properties of the oil or grease but also mitigates the risk of thermal degradation and premature wear of gearbox components. Ultimately, effective heat dissipation contributes to the overall reliability, longevity, and performance consistency of the gearbox assembly.
Protection of Lubrication System: One of the primary functions of the gearbox housing is to serve as a robust protective shield for the internal lubrication system. The housing effectively shields the lubricant and sensitive gearbox components from external contaminants, environmental factors, and mechanical hazards that could compromise the integrity and performance of the lubrication system. By creating a barrier against ingress of contaminants such as dirt, moisture, abrasive particles, and chemical agents, the housing helps maintain a clean and controlled operating environment within the gearbox. This protective barrier significantly reduces the risk of lubricant contamination, abrasive wear, corrosion, and other detrimental effects that could impair gearbox performance and reliability. As a result, the housing enhances the operational robustness, durability, and overall effectiveness of the gearbox assembly in demanding industrial applications.