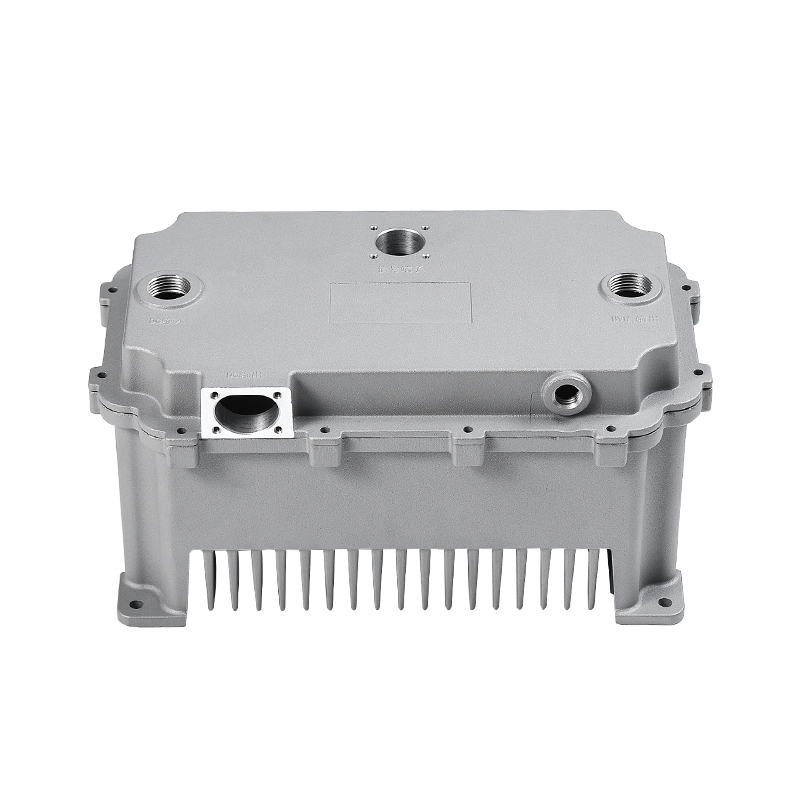
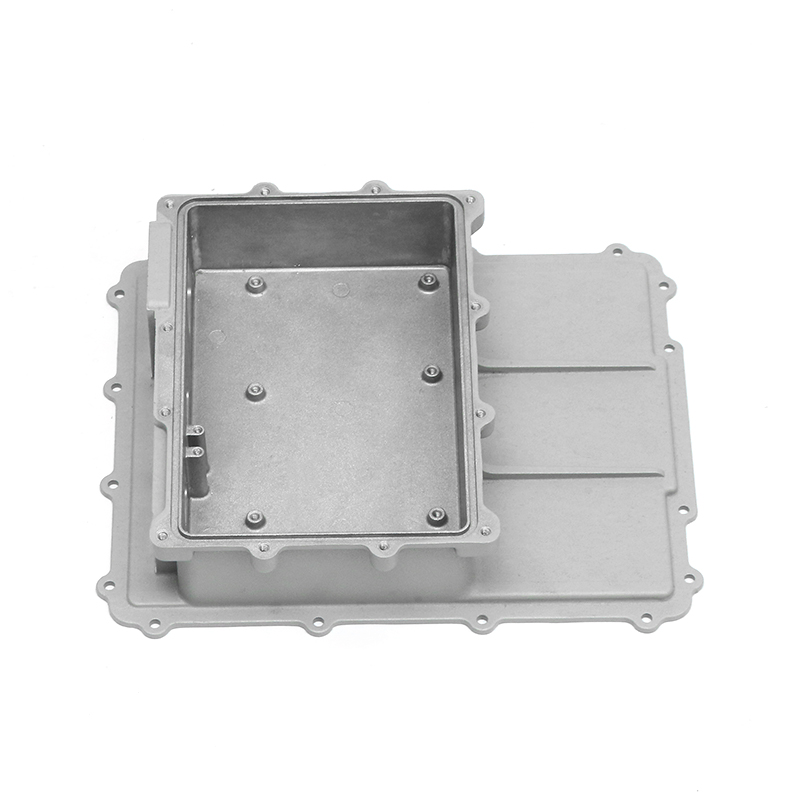
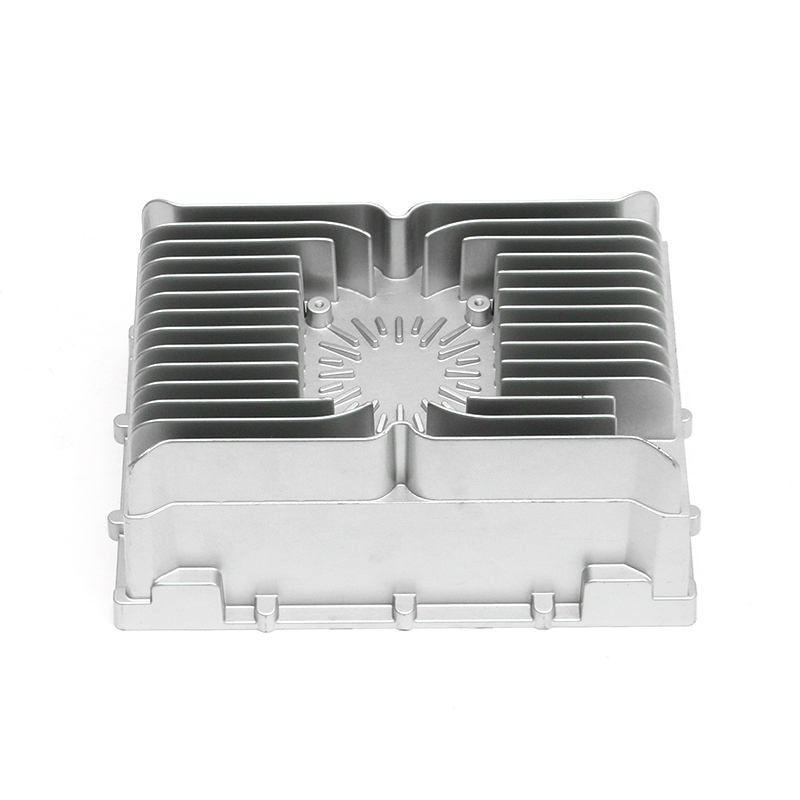
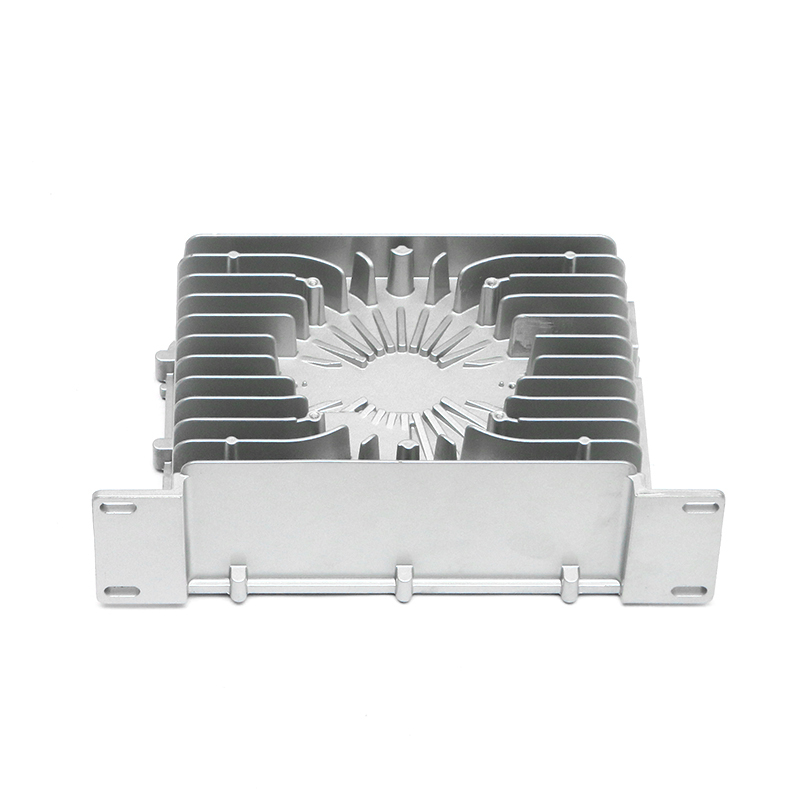
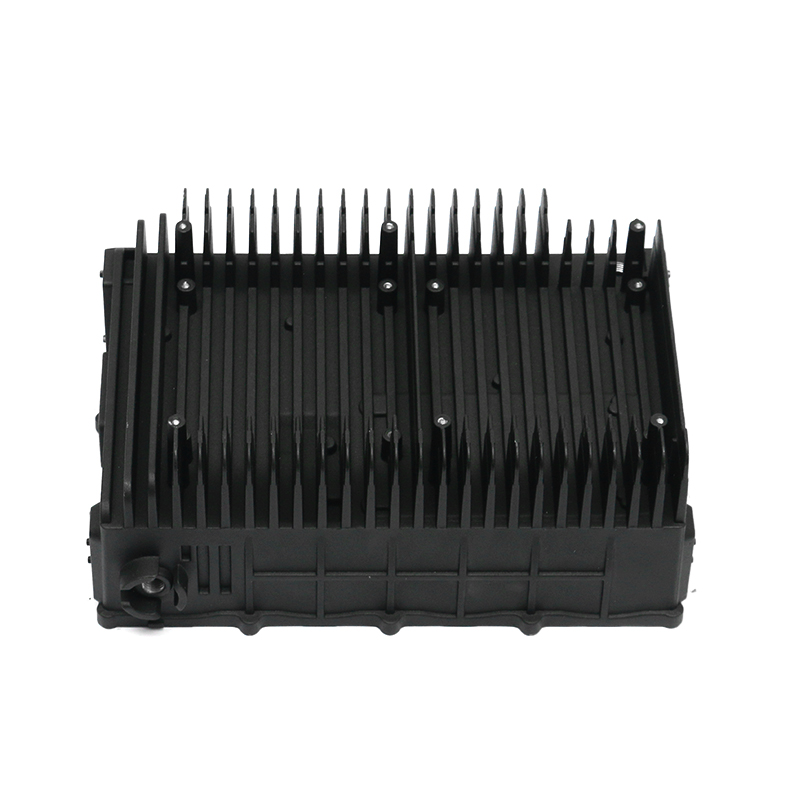
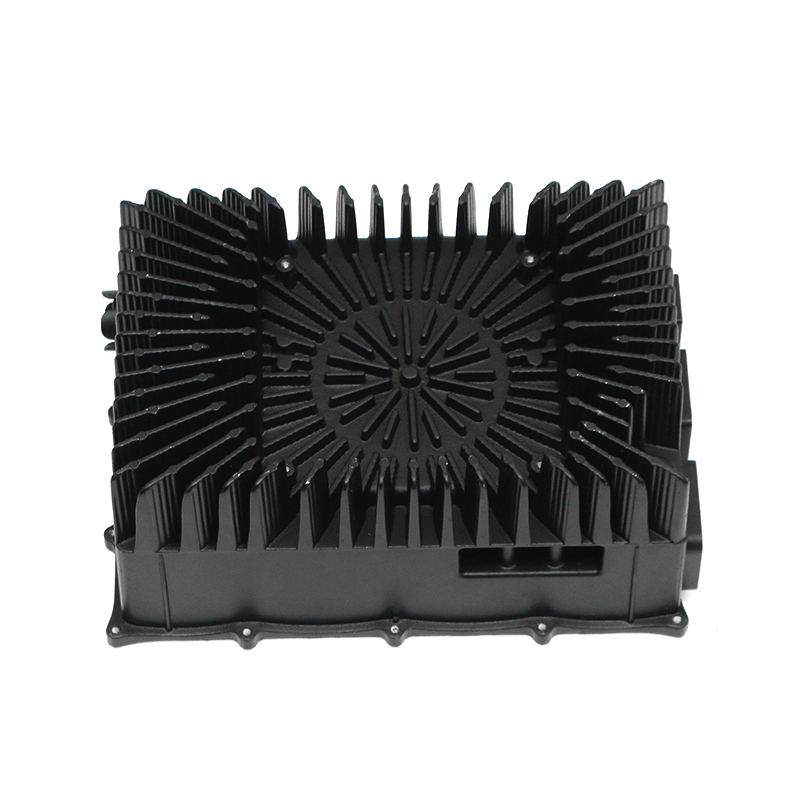
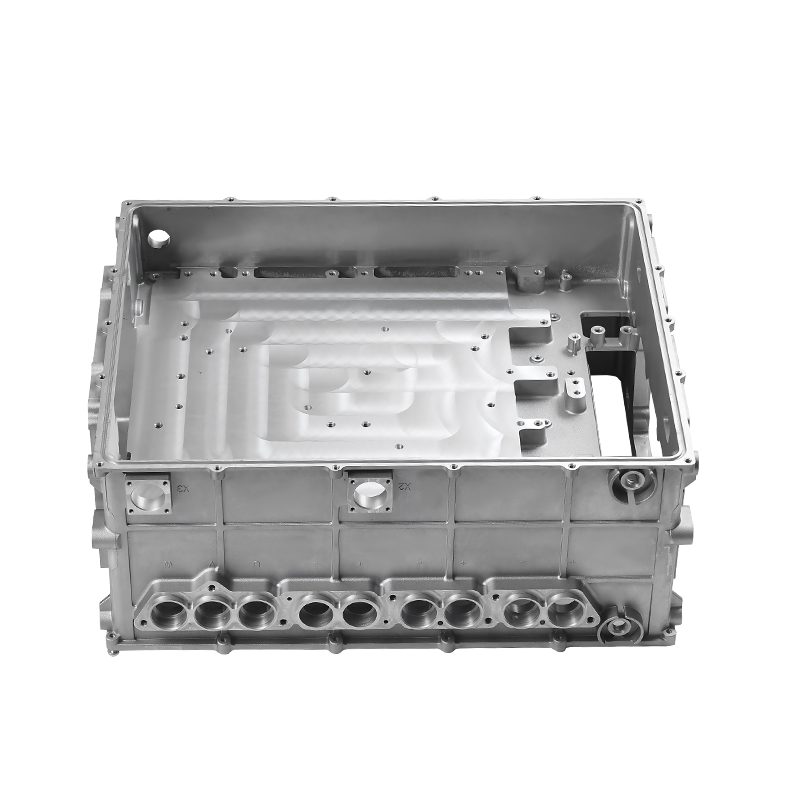
The gearbox housing plays a key role in the gearbox system. It not only carries the complex internal gear mechanism and lubrication system, but also plays an important role in the heat dissipation process. The gearbox generates heat during operation, which mainly comes from the friction of the gears, the operation of the bearings and the circulation of the lubricating oil. A reasonable housing structure can effectively improve the heat dissipation effect, thereby improving the overall working performance of the gearbox.
The material selection of the housing has a certain influence on the heat dissipation performance. Usually, metal materials with good thermal conductivity are used so that the housing can quickly conduct and dissipate the heat generated inside. In addition, the thickness and density of the housing will also affect its heat dissipation capacity. The appropriate wall thickness can take into account both strength and thermal conductivity, so that the heat can be evenly transferred outward without accumulating in local areas.
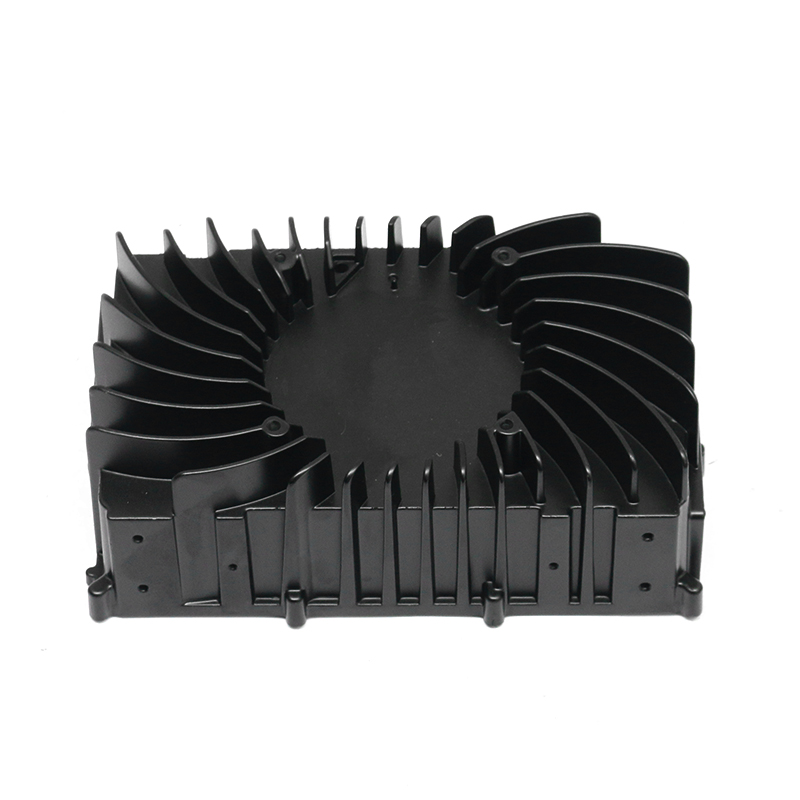
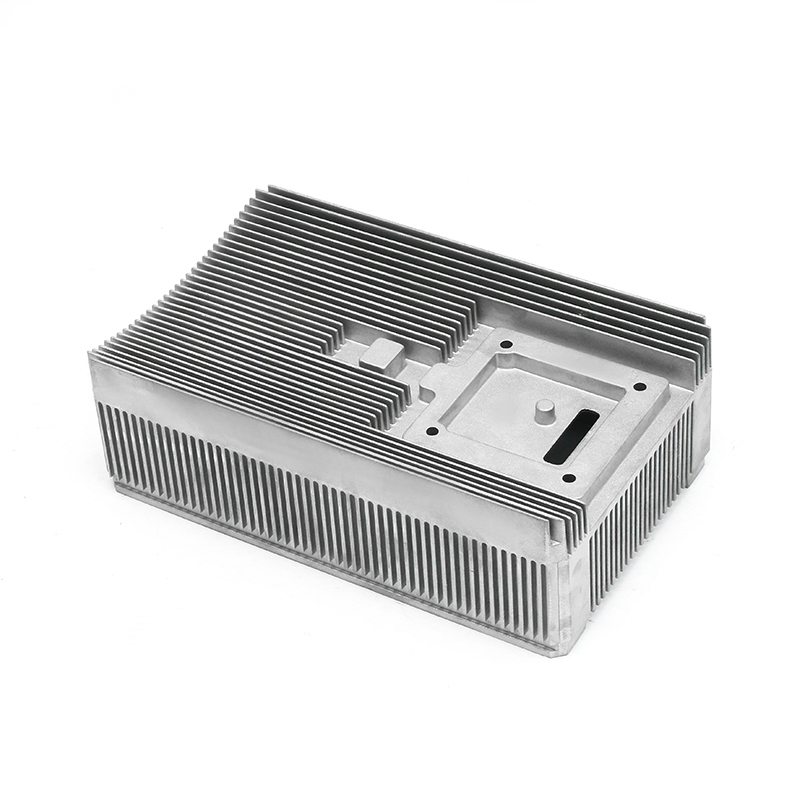
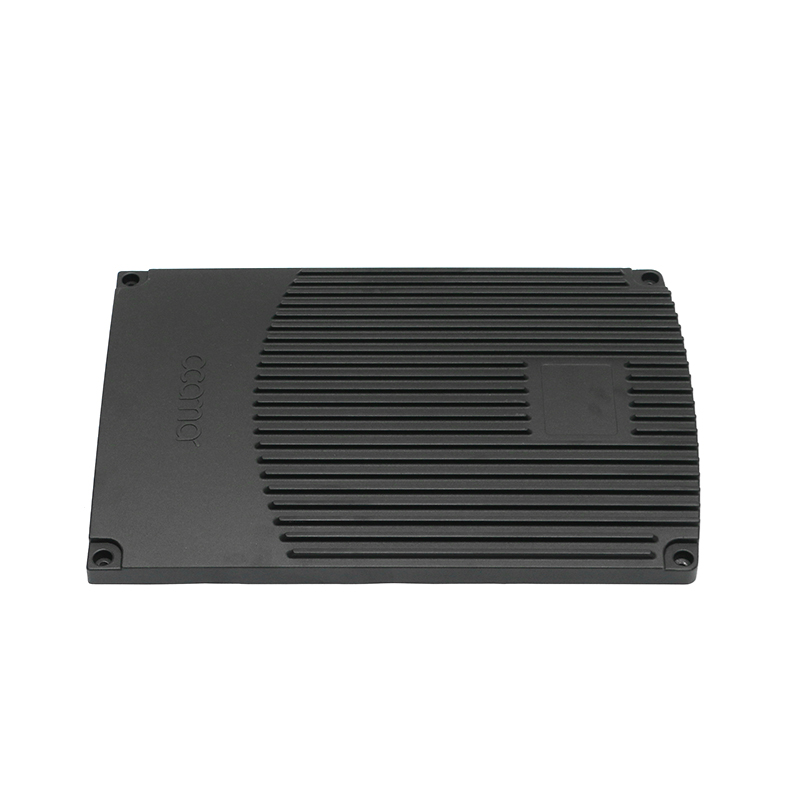
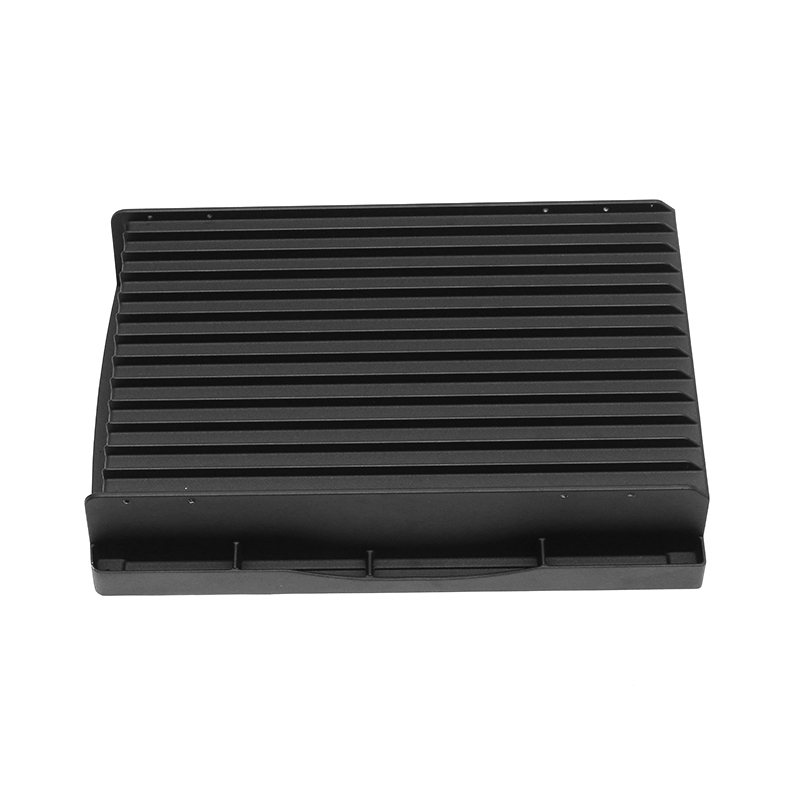
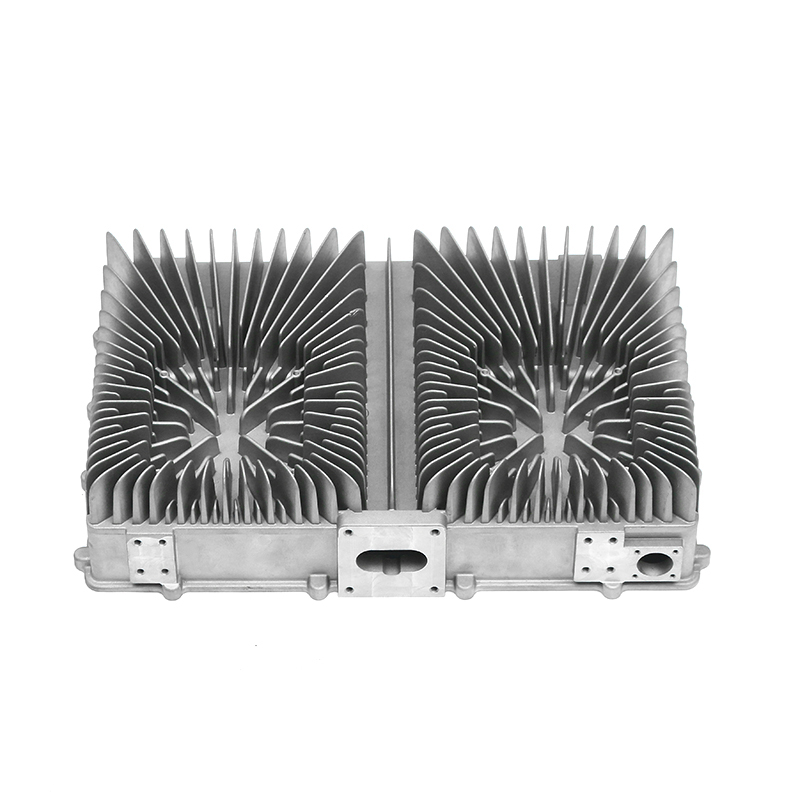
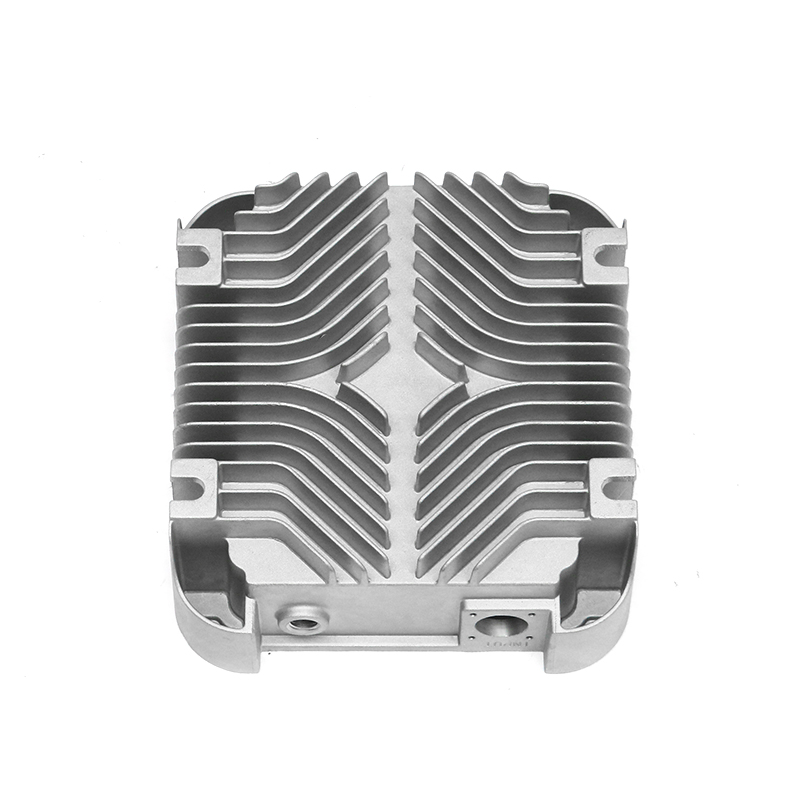
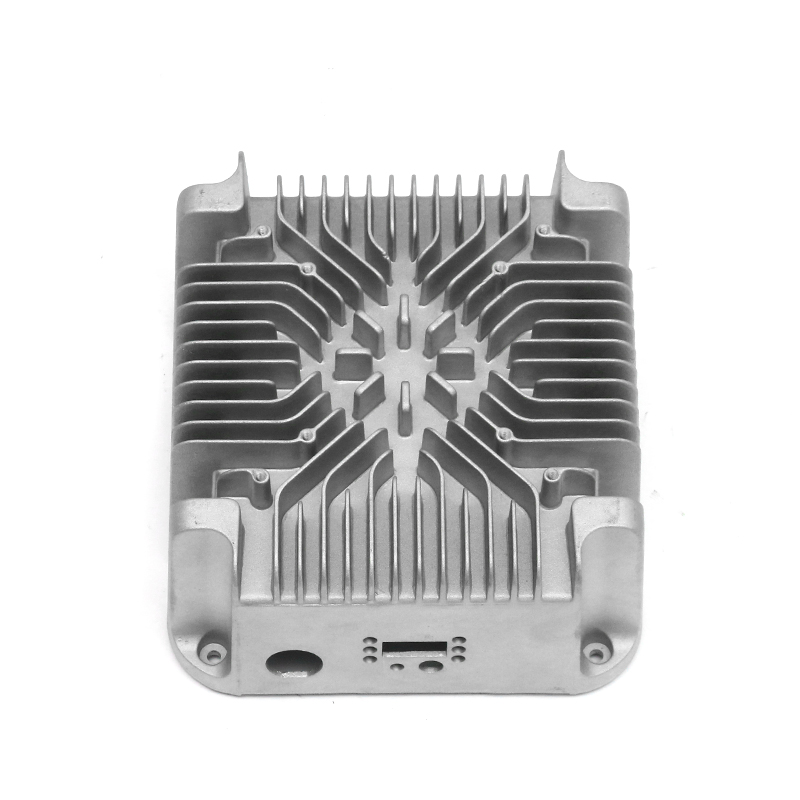
In terms of the external design of the housing, the optimization of the heat dissipation structure can effectively improve the heat release efficiency. The surface adopts a specific design, such as heat dissipation ribs or heat sinks, so that the contact area of the housing is increased, thereby accelerating the speed of heat diffusion outward. This method can not only reduce the internal temperature of the gearbox, but also reduce the degradation of lubricating oil performance caused by high temperature, thereby extending the service life of the gearbox.
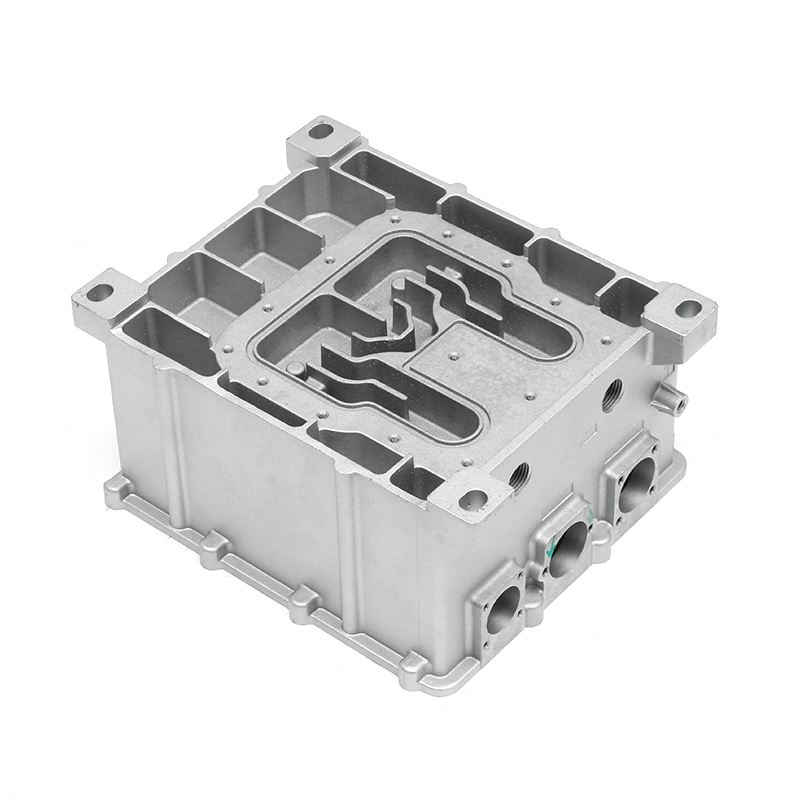
The design inside the housing also has an important influence on the heat dissipation effect. Reasonable oil channel design allows lubricating oil to circulate efficiently between gears and bearings, so that the heat generated by friction can be removed in time. Smooth oil channels reduce the situation of local overheating, so that the inside of the gearbox remains in a relatively stable working state. Some housings are also equipped with a guide structure inside to guide air or lubricating oil to flow along a specific path, so that heat can be evenly diffused and prevent the appearance of high-temperature areas.
The ventilation design of the gearbox housing also plays a positive role in the heat dissipation process. Reasonable air inlets and outlets allow air to circulate around the housing to accelerate the dissipation of heat. For some gearboxes that require additional heat dissipation, cooling devices such as oil cooling systems will also be equipped, so that the lubricating oil can take away heat more efficiently and further improve the heat dissipation performance.
In terms of installation, the layout and fixing method of the housing will also affect the heat dissipation effect. Reasonable installation angles can expose the heat dissipation surface to an area that is more conducive to air circulation and reduce heat accumulation. In addition, the matching design with other components also needs to consider the heat dissipation requirements to avoid affecting the fluidity of the air, so as to ensure that the entire system can operate efficiently.
Recommended Products
Products provided by famous enterprises are deeply trusted by users.