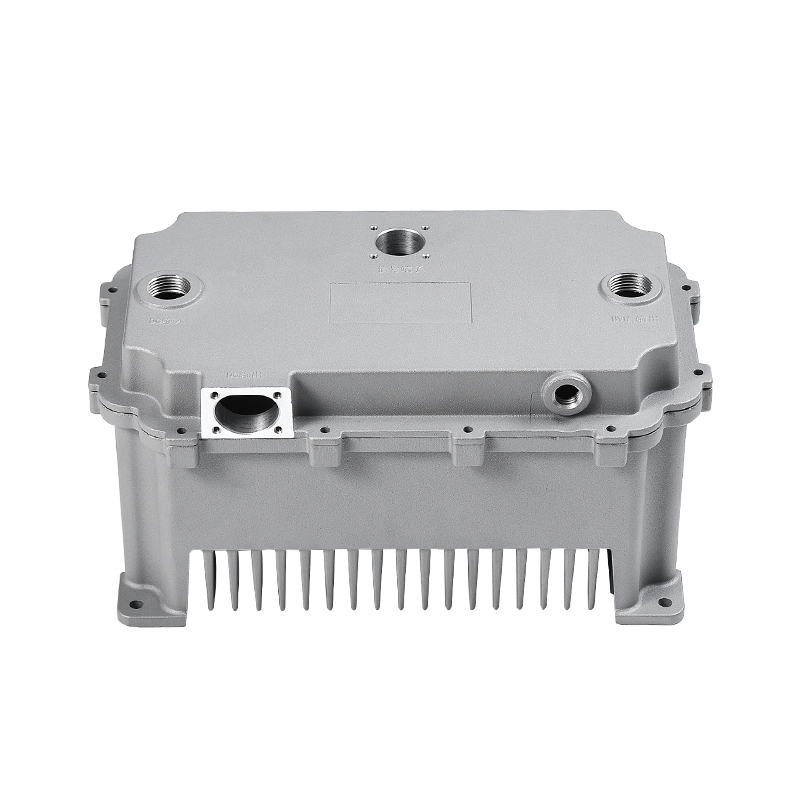
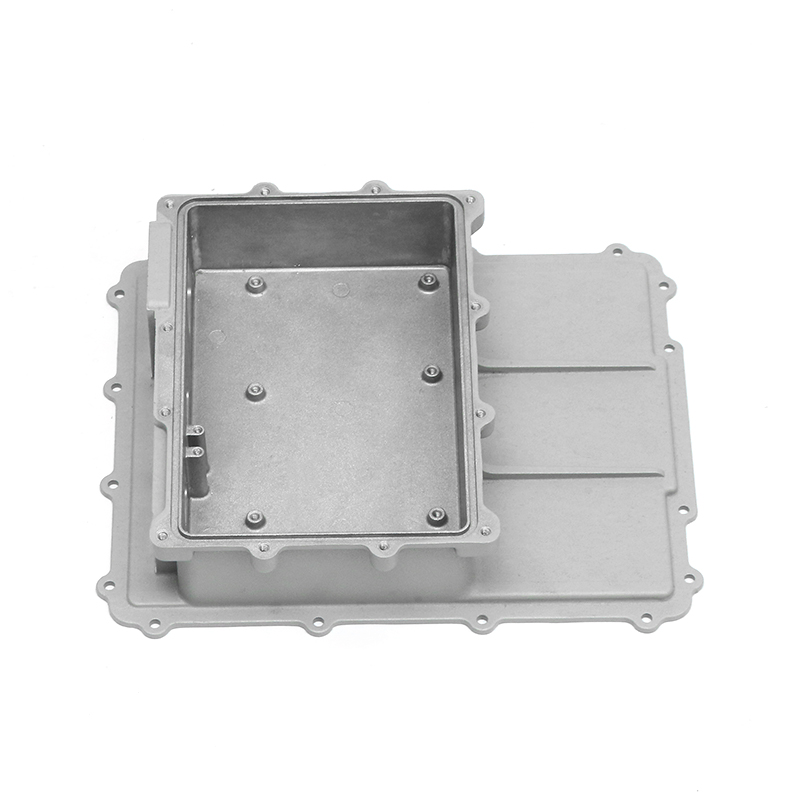
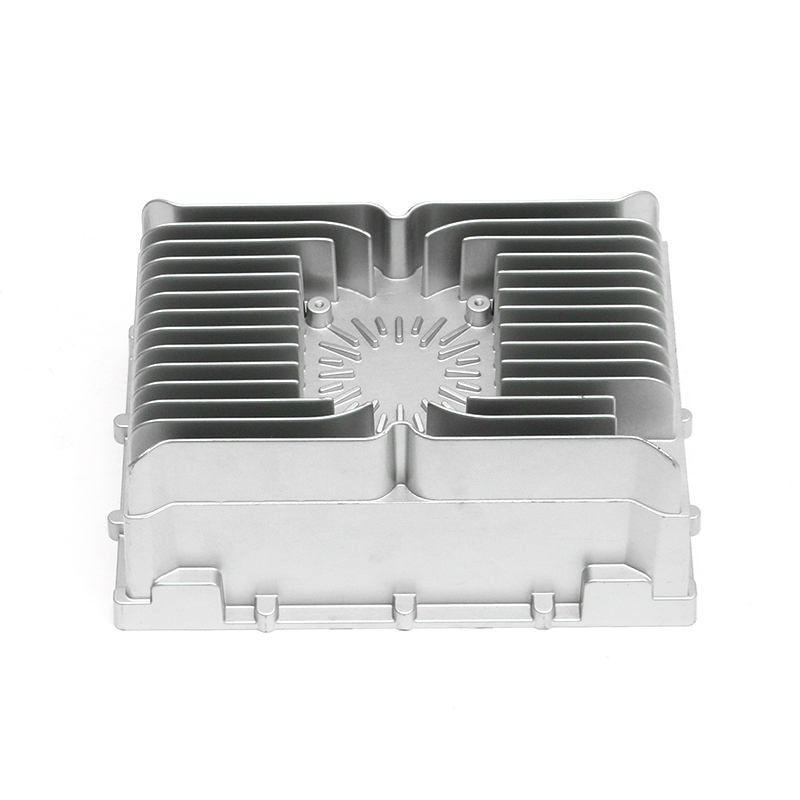
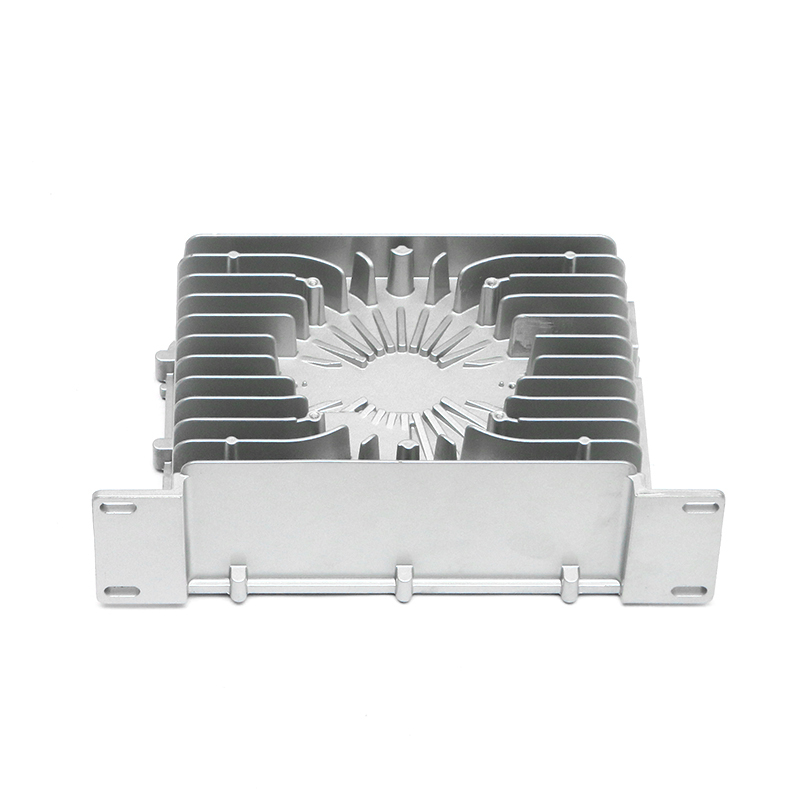
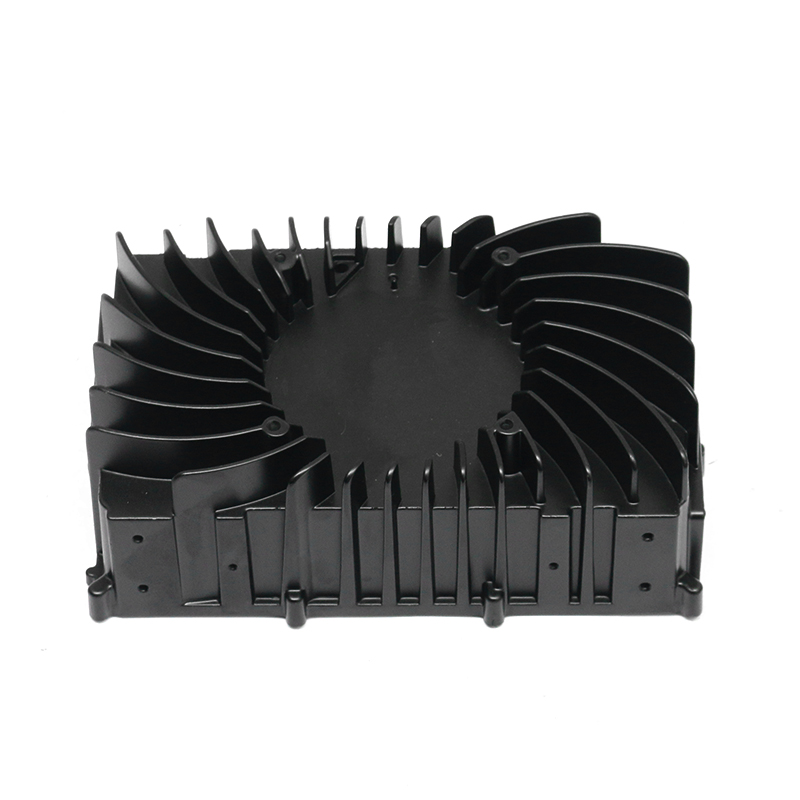
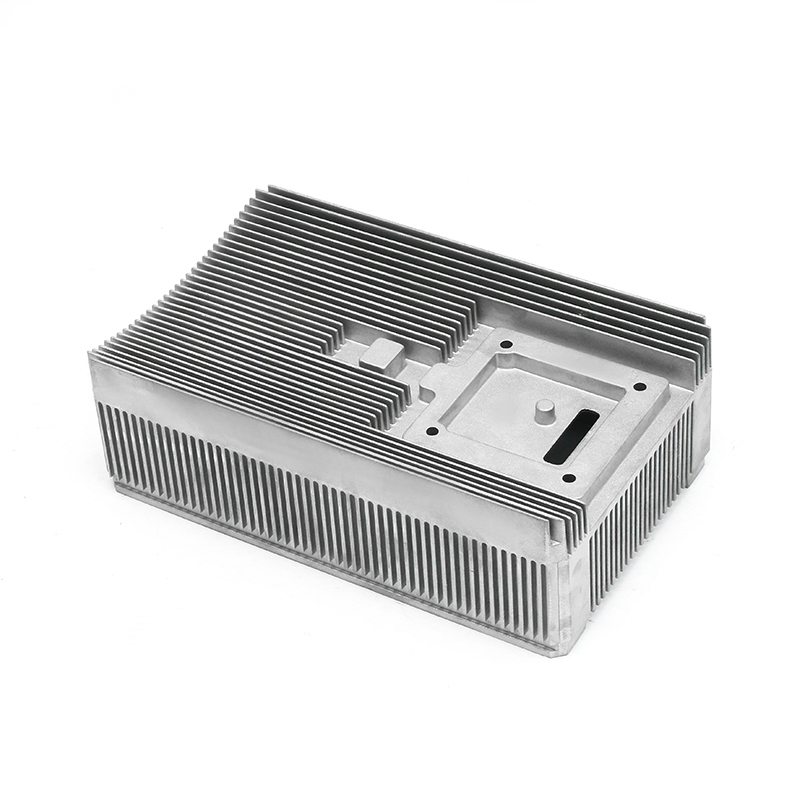
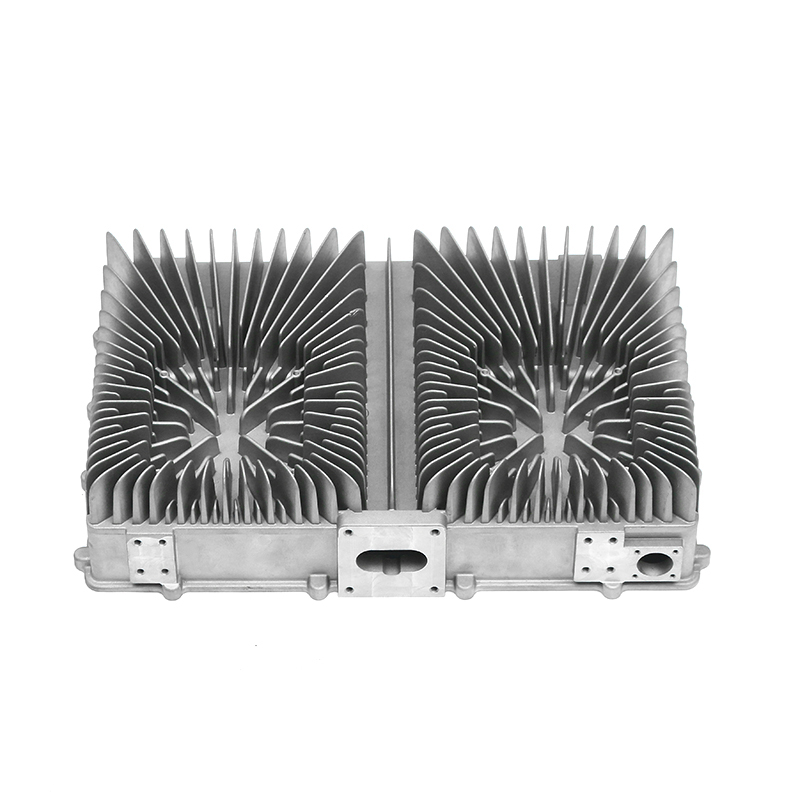
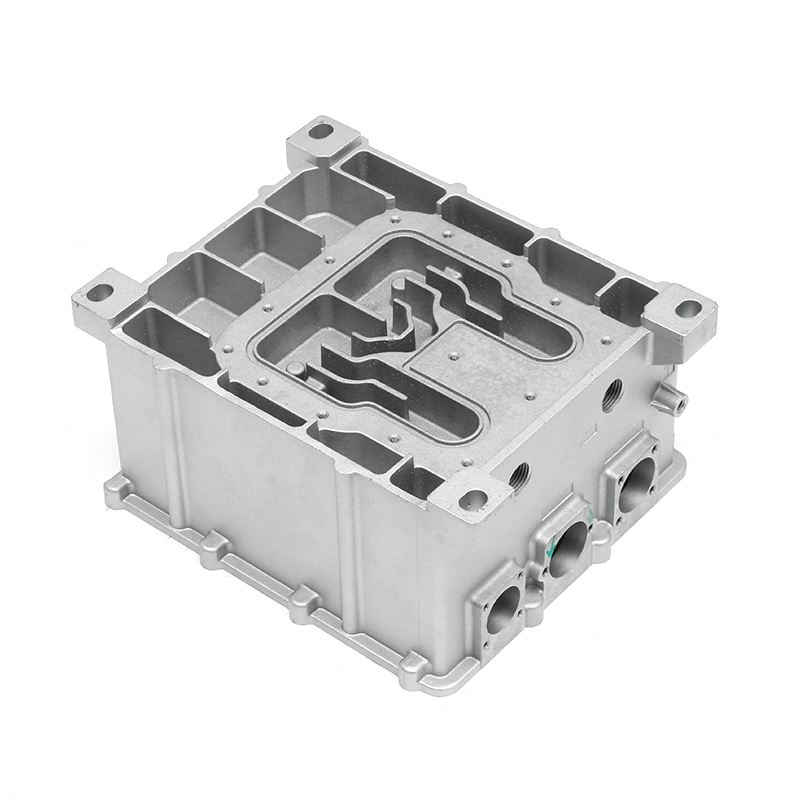
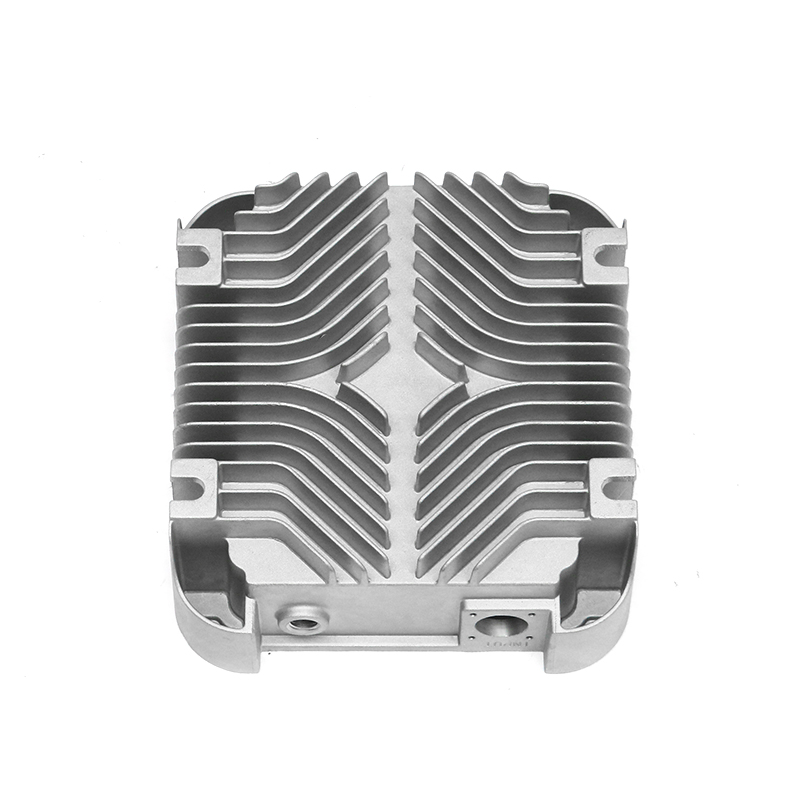
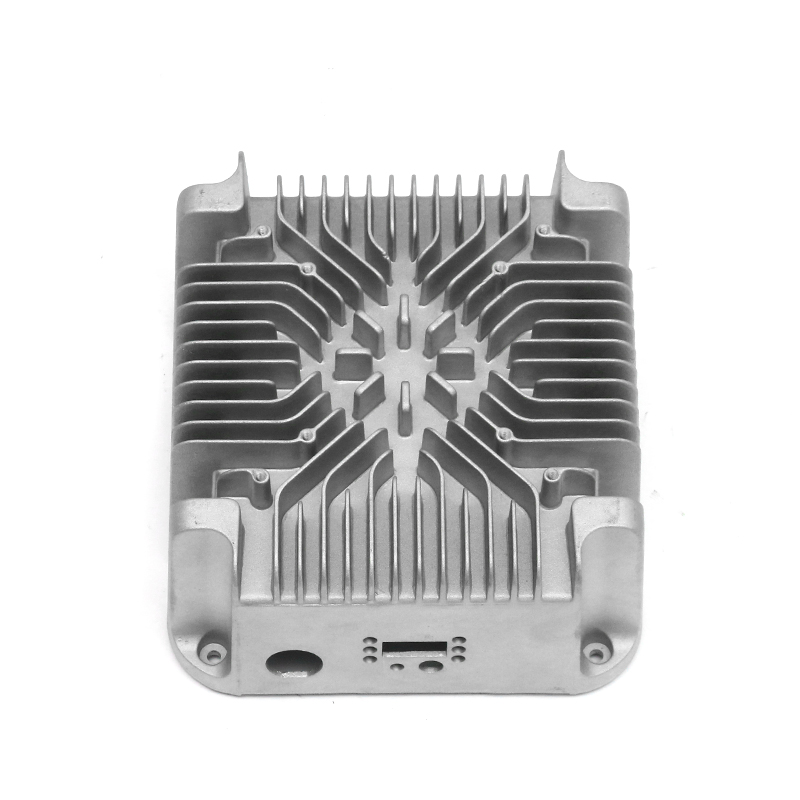
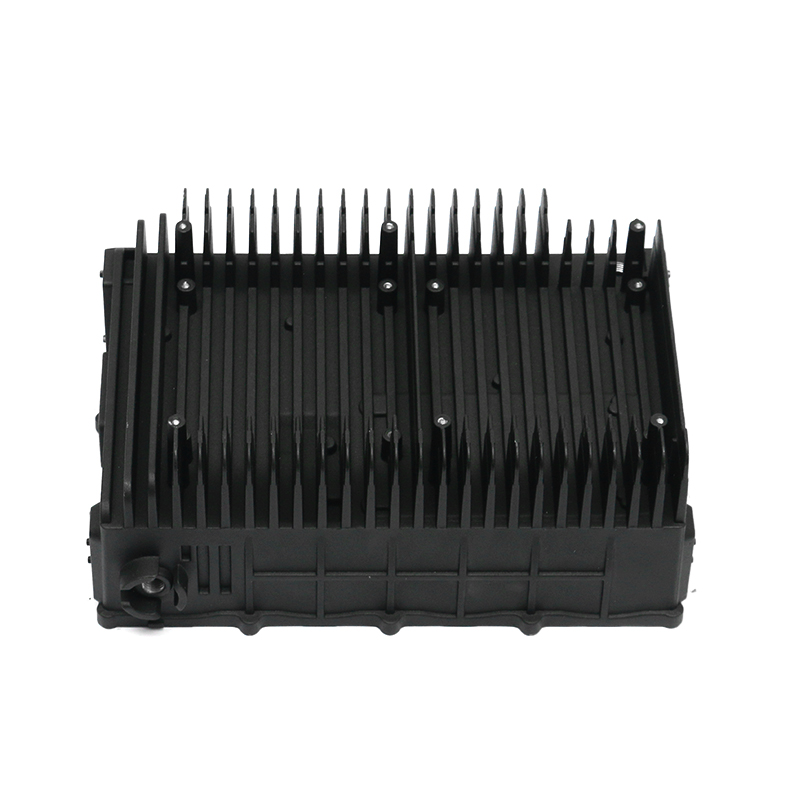
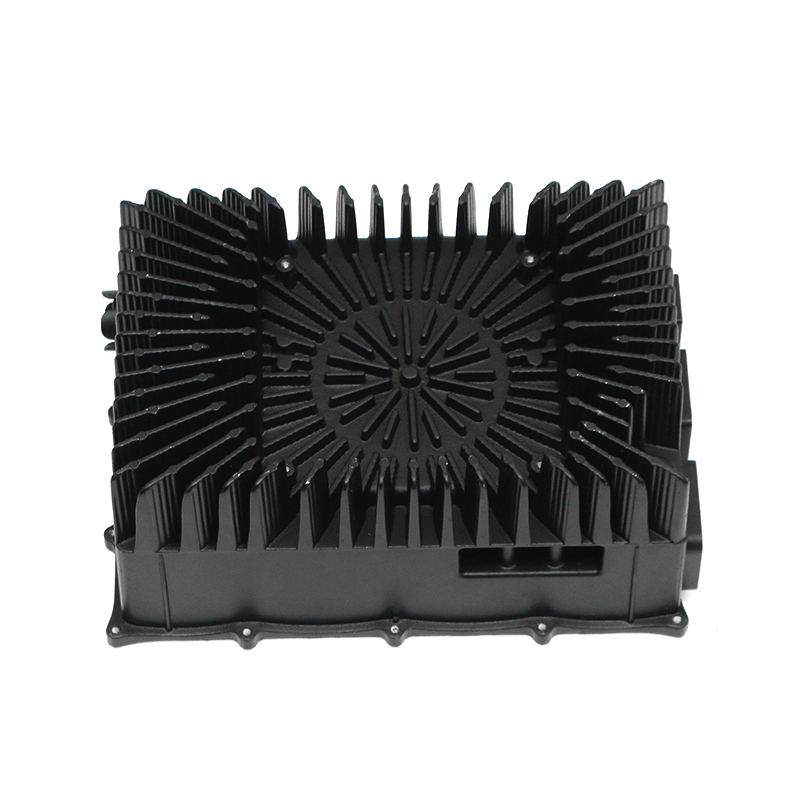
The precision trimming mold ensures the accuracy of trimmed parts through several key design features and mechanisms that work together to maintain tight tolerances and consistent quality throughout the molding process.
Precision Engineering: The mold is designed to exact specifications, with very tight tolerances that are engineered to ensure parts are trimmed to the required dimensions. This means that the mold components (such as cutting edges, inserts, and guides) are manufactured with extremely high precision, reducing the risk of inaccuracies during trimming.
Specialized Cutting Edges: The trimming mold uses sharp, high-quality blades or cutting surfaces that are designed for precise cuts. These cutting edges are often made from durable materials like tungsten carbide or hardened steel, ensuring clean and accurate trimming without distortion.
Fixed Part Positioning: Accurate trimming requires that the workpiece is securely held in place during the operation. The mold often includes advanced alignment and clamping systems that ensure the part is correctly positioned every time, preventing shifts or movement that could cause inaccurate trimming.Automated Adjustments: Some precision trimming molds feature automated systems that adjust part positioning as needed, further improving the accuracy of the trimming process.
Long-lasting Precision: The mold is typically constructed from high-quality, wear-resistant materials that maintain their dimensions and sharpness over time. This helps prevent errors or degradation in trimming accuracy due to wear and tear.Replacements for Key Components: In many cases, parts such as cutting blades or inserts are replaceable, ensuring that the mold continues to perform accurately throughout its life cycle. Regularly replacing worn-out components helps maintain the mold’s precision.
Pressure Regulation: Precision trimming molds often have pressure control systems that ensure the trimming operation occurs under consistent and precise force. Variations in pressure can lead to inaccurate cuts, but by maintaining stable conditions, the mold ensures parts are trimmed accurately to specification.
Temperature Control: In some cases, the mold may also incorporate temperature regulation mechanisms. Temperature changes can cause materials to expand or contract, affecting trim accuracy. Temperature control ensures that the mold operates within an optimal thermal range, minimizing dimensional variations.
Interchangeable Inserts: The use of precision inserts or molds that can be easily replaced or adjusted allows for fine-tuning of the trimming process. These inserts are designed to maintain precise cutting edges and can be customized to suit specific part geometries, ensuring accuracy across different product designs.
Minimal Gap Between Cutting Surfaces: The mold is designed to minimize the gap between the cutting edges, reducing the chances of part movement during trimming. A small gap ensures that the cut is more accurate and reduces the potential for burrs or uneven surfaces.Precision Guides and Bushings: Precision trimming molds often feature guides and bushings that ensure the cutting components remain in exact alignment throughout the operation. These components help direct the force of the trimming process, preventing the tool from deviating from the intended path.
Recommended Products
Products provided by famous enterprises are deeply trusted by users.